Chapter Summary
Chapter Summary
Section 1: Business Cycles
Business cycles are the alternating increases and decreases in economic activity typical of market economies.
Business cycles can vary in duration and intensity, just like a roller coaster. These fluctuations take place around a long-run growth trend.
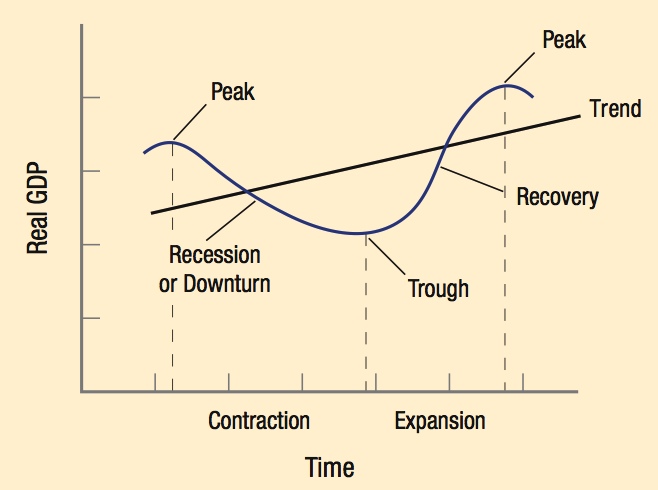
Business cycles are officially dated by the National Bureau of Economic Research, which assigns a committee of economists to determine “turning points” when the economy switches from peak to recession or from trough to recovery. They do this using past data, which means announcements take place after the turning points occur.
Four Phases of the Business Cycle
- Peak: The economy is operating at its capacity.
- Recession: Occurs when the economy runs out of steam and business investment falls.
- Trough: The economy reaches the depth of the recession.
- Recovery: Economic activity picks up and the economy grows.
Alternative Measures of Business Cycles
- National Activity Index
- Leading Economic Index
- Yield Curve
Section 2: National Income Accounting
The national income and product accounts (NIPA) allow economists to judge our nation’s economic performance, compare income and output to that of other nations, and track the economy’s condition over the course of the business cycle.
Gross domestic product (GDP) is the total market value of all final goods and services produced in a year within a country’s borders, regardless of a firm’s nationality. Gross national product (GNP) measures goods produced by a country’s firms, regardless of where they are produced.

U.S. firm; made in USA
Part of U.S. GDP and GNP

U.S. firm; made in China
Part of U.S. GNP, not GDP
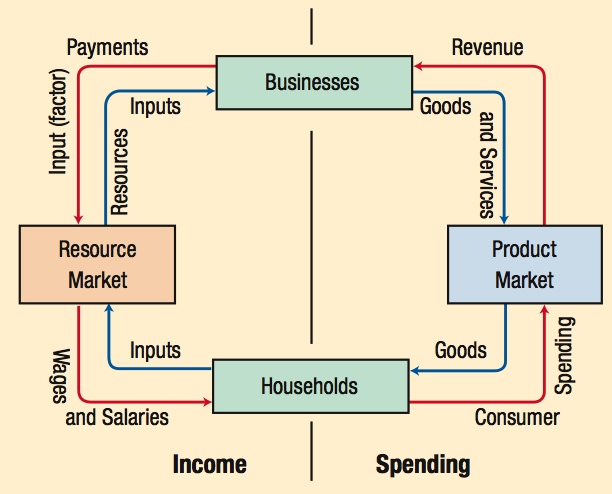
The circular flow diagram shows how businesses and households interact through the resource and product markets. It shows spending as well as income.
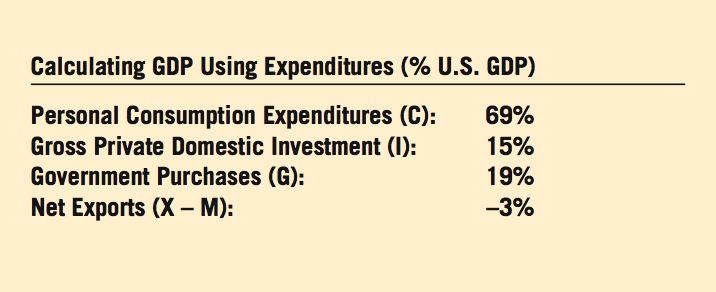
The major components of the NIPA can be constructed in either of two ways: by summing the spending of the economy or by summing income. Likewise, GDP can be measured by adding together either spending or income.

Section 3: GDP and Our Standard of Living
GDP per capita is measured as GDP divided by the population. It provides a rough measure of a country’s standard of living relative to other countries. However, it does not reflect differences in wealth within a country.
Countries are placing greater emphasis on protecting the environment. The economic benefits from a clean environment, however, are mostly unmeasured in GDP statistics. This is changing as new measures are introduced to take environmental quality and degradation into account.

The informal economy includes all market transactions that are not officially reported and hence are not included in GDP measures; it creates both positive and negative effects:
- Positive: Transactions in an informal economy create jobs and contribute to overall economic activity
- Negative: Taxes are rarely paid on income in the informal economy, putting a greater tax burden on others. Also, the informal economy is less regulated, which can lead to unsafe products or risky job conditions.


