Chapter Summary
Chapter Summary
Section 1: Inflation
Inflation is a measure of the general rise in prices throughout the economy. Prices for individual goods can fluctuate up or down, but the price level captures the overall trend in the movement of prices.
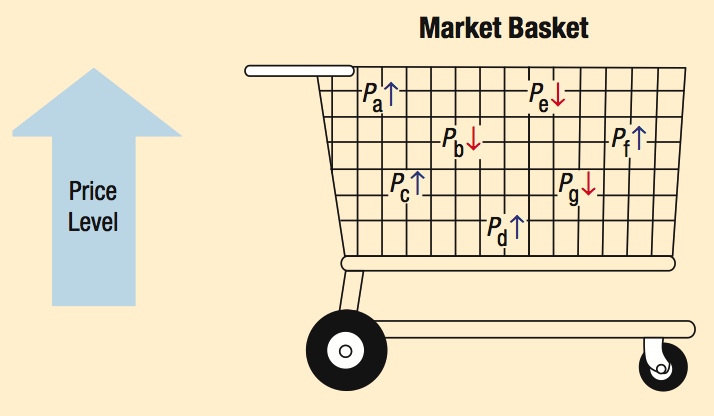
How Inflation Is Measured
- Consumer price index (CPI): Measures the average change in prices of a market basket of consumer goods and services.
- Producer price index (PPI): Measures the average change in prices received by producers for their output.
- GDP deflator: The broadest measure of inflation, measuring the prices of all goods and services in the economy.
Calculating Inflation Using the CPI
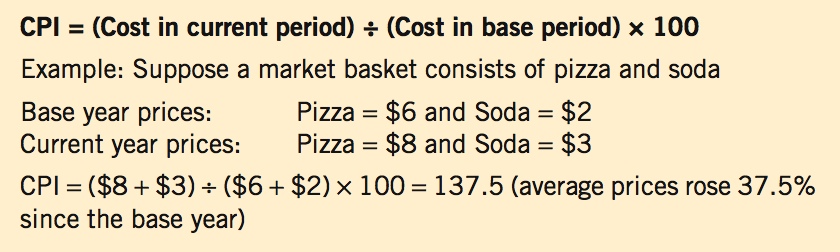

The Main Causes of Inflation
- Strong consumer demand: Consumers spend more money, demand increases, and prices rise.
- Supply shocks on key inputs: Prices for inelastic goods such as food and inputs such as oil rise; higher prices are passed on to other industries and to consumers.
- Government printing money: The government prints money to finance its borrowing, more money is chasing a relatively fixed amount of goods and services, and therefore prices rise.

Disinflation Versus Deflation
Disinflation occurs when the rate of inflation falls, but is still positive.
Deflation occurs when the rate of inflation turns negative.
Hyperinflation is an extremely high rate of inflation. It typically is caused by excess government spending over tax revenues (high deficits) and the printing of money to finance deficits.
Section 2: Unemployment

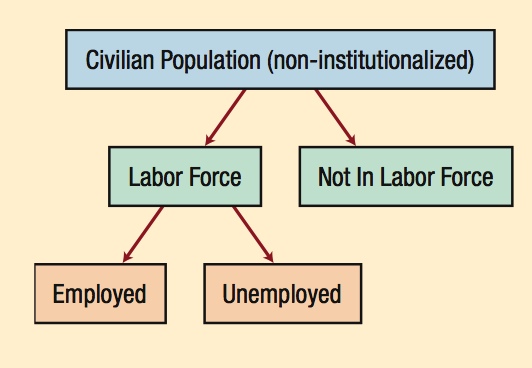
The labor force is the total number of people employed or unemployed. Employed persons are individuals age 16 and over who work for pay, whether full time, part time, or even temporary. Unemployed persons are those without jobs but are actively seeking work.
What About Everyone Else?
Discouraged workers are those who have given up actively looking for work, and are not counted as unemployed.
Students who do not work are not counted in the labor force.
Retired persons and children under 16 are not counted in the labor force.
Institutionalized persons including persons in prison also are not counted in the labor force.
Section 3: Unemployment and the Economy
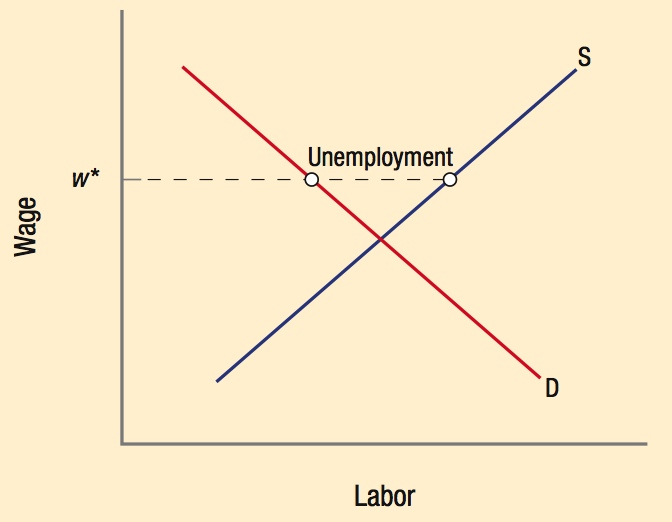
The natural rate of unemployment (NAIRU) is the rate of unemployment that exists when prices and wages are equal to people’s expectations. At the NAIRU, the economy is at “full employment.”
NAIRU = frictional + structural unemployment
NAIRU is very stable in the United States at around 5% to 6%.

Types of Unemployment
- Frictional unemployment: Includes workers who voluntarily quit their jobs in search of better positions, or recent graduates seeking their first high-paying job.
- Structural unemployment: Longer term unemployment that is caused by changes in consumer demands or technology, and requires workers to be retrained for a career in another industry.
- Cyclical unemployment: Unemployment that results from the business cycle—when a recession hits, firms lay off workers until the economy recovers.