Questions and Problems
Check Your Understanding
Question
Describe the impact of rising interest rates on consumer spending.
Prob 20 1. Describe the impact of rising interest rates on consumer spending.Question
When the economy is operating at full employment, why is an increase in aggregate demand not helpful to the economy?
Prob 20 2. When the economy is operating at full employment, why is an increase in aggregate demand not helpful to the economy?Question
When the economy is hit with a supply shock, such as oil prices rising from $25 a barrel to $75 a barrel, why is this doubly disruptive and harmful to the economy?
Prob 20 3. When the economy is hit with a supply shock, such as oil prices rising from $25 a barrel to $75 a barrel, why is this doubly disruptive and harmful to the economy?When the economy is operating at full employment, why is an increase in aggregate demand not helpful to the economy?Question
Explain why the aggregate supply curve is positively sloped during the short run and vertical in the long run.
Prob 20 4. Explain why the aggregate supply curve is positively sloped during the short run and vertical in the long run.When the economy is operating at full employment, why is an increase in aggregate demand not helpful to the economy?Question
List some examples of factors that will shift the aggregate demand curve.
Prob 20 5. List some examples of factors that will shift the aggregate demand curve.When the economy is operating at full employment, why is an increase in aggregate demand not helpful to the economy?Question
List some examples of factors that will shift the long-run aggregate supply curve.
Prob 20 6. List some examples of factors that will shift the long-run aggregate supply curve.When the economy is operating at full employment, why is an increase in aggregate demand not helpful to the economy?
Apply the Concepts
Question
There is little doubt that computers and the Internet have changed our economy. Information technology (IT) can boost efficiency in nearly everything: Markets are more efficient, IT is global, and IT improves the design, manufacture, and supply chain of products we produce. Use the aggregate demand and supply framework discussed in this chapter to show the impact of IT on the U.S. economy.
Prob 20 7. There is little doubt that computers and the Internet have changed our economy. Information technology (IT) can boost efficiency in nearly everything: Markets are more efficient, IT is global, and IT improves the design, manufacture, and supply chain of products we produce. Use the aggregate demand and supply framework discussed in this chapter to show the impact of IT on the U.S. economy.When the economy is operating at full employment, why is an increase in aggregate demand not helpful to the economy?Question
Unemployment can be caused by a reduction in aggregate demand or short-run aggregate supply. Both changes are represented by a leftward shift in the curves. Does it matter whether the shift occurs in aggregate demand or short-run aggregate supply? Use the AD/AS framework to show why or why not.
Prob 20 8. Unemployment can be caused by a reduction in aggregate demand or short-run aggregate supply. Both changes are represented by a leftward shift in the curves. Does it matter whether the shift occurs in aggregate demand or short-run aggregate supply? Use the AD/AS framework to show why or why not.When the economy is operating at full employment, why is an increase in aggregate demand not helpful to the economy?Question
Why is cost-push inflation a more difficult problem for policymakers than demand-pull inflation?
Prob 20 9. Why is cost-push inflation a more difficult problem for policymakers than demand-pull inflation?When the economy is operating at full employment, why is an increase in aggregate demand not helpful to the economy?Question
Why is consumer confidence so important in determining the equilibrium level of output and employment?
Prob 20 10. Why is consumer confidence so important in determining the equilibrium level of output and employment?When the economy is operating at full employment, why is an increase in aggregate demand not helpful to the economy?Question
As the Japanese yen appreciated in value during the 1980s and 1990s, more Japanese auto companies built manufacturing plants in other parts of Asia and in the United States. What impact did this have on net exports for the United States? Why did Japanese automakers build plants in the United States? Were the reasons similar to the reasons that American firms build plants (or establish offshore production) in China and other parts of Asia?
Prob 20 11. As the Japanese yen appreciated in value during the 1980s and 1990s, more Japanese auto companies built manufacturing plants in other parts of Asia and in the United States. What impact did this have on net exports for the United States? Why did Japanese automakers build plants in the United States? Were the reasons similar to the reasons that American firms build plants (or establish offshore production) in China and other parts of Asia?When the economy is operating at full employment, why is an increase in aggregate demand not helpful to the economy?Question
Some advocates have suggested that the United States should move to a universal health care plan paid for at the federal level, like Medicare, which would be funded out of general tax revenues. Such a plan, it is argued, would guarantee quality health care to all. Ignoring all the controversy surrounding such a plan, would the introduction of universal health care paid for from general revenues have an impact on short-run aggregate supply? On long-run aggregate supply? Why or why not?
Prob 20 12. Some advocates have suggested that the United States should move to a universal health care plan paid for at the federal level, like Medicare, which would be funded out of general tax revenues. Such a plan, it is argued, would guarantee quality health care to all. Ignoring all the controversy surrounding such a plan, would the introduction of universal health care paid for from general revenues have an impact on short-run aggregate supply? On long-run aggregate supply? Why or why not?When the economy is operating at full employment, why is an increase in aggregate demand not helpful to the economy?
In the News
Question
Oil production in the United States has increased significantly over the past decade as a result of improved oil extraction technologies, with some analysts predicting that the United States will surpass Saudi Arabia in overall energy production by the end of the decade (“U.S. Oil Output to Overtake Saudi Arabia’s by 2020,” Bloomberg.com, November 12, 2012). How do the increase in U.S. energy production and the subsequent reduction in the reliance on imported oil affect the U.S. aggregate demand and/or aggregate supply curves?
Prob 20 13. Oil production in the United States has increased significantly over the past decade as a result of improved oil extraction technologies, with some analysts predicting that the United States will surpass Saudi Arabia in overall energy production by the end of the decade (“U.S. Oil Output to Overtake Saudi Arabia’s by 2020,” Bloomberg.com, November 12, 2012). How do the increase in U.S. energy production and the subsequent reduction in the reliance on imported oil affect the U.S. aggregate demand and/or aggregate supply curves?When the economy is operating at full employment, why is an increase in aggregate demand not helpful to the economy?Question
In early 2013, significant political gridlock in Congress involved automatic spending cuts by the government termed the Sequester. Many economists warned that allowing the drastic cuts to persist increased the risk of another recession (“The Sequester and Fiscal Policy,” The New York Times, March 8, 2013). Using the AD/AS model and what you know about the multiplier, explain why economists would come to this conclusion.
Prob 20 14. In early 2013, significant political gridlock in Congress involved automatic spending cuts by the government termed the Sequester. Many economists warned that allowing the drastic cuts to persist increased the risk of another recession (“The Sequester and Fiscal Policy,” The New York Times, March 8, 2013). Using the AD/AS model and what you know about the multiplier, explain why economists would come to this conclusion.When the economy is operating at full employment, why is an increase in aggregate demand not helpful to the economy?
Solving Problems
- In the figure below, the economy is initially in equilibrium at full employment at point e. Assume that consumption falls by 100, leading to a shift in aggregate demand from AD0 to AD1.
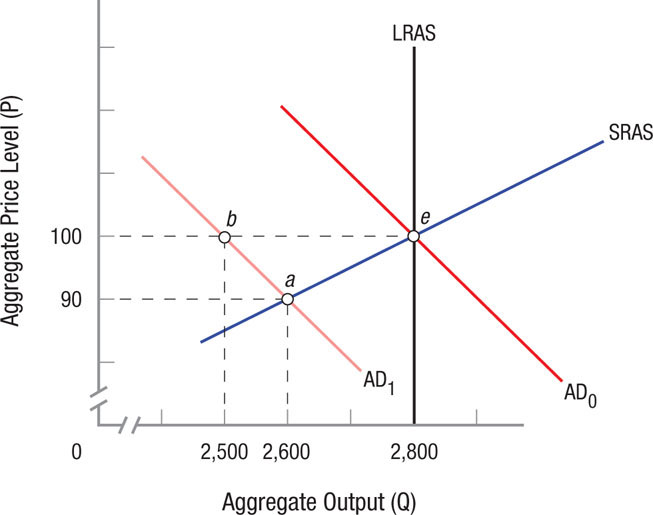
Question
What is the new short-run equilibrium?
Prob 20 15a. What is the new short-run equilibrium?Question
How large is the simple Keynesian multiplier in this case?
Prob 20 15b. How large is the simple Keynesian multiplier in this case?
- Use the table and grid below to answer the following questions:
Question
In the grid, graph the aggregate demand and short-run aggregate supply curves (label them AD0 and SRAS0). What are equilibrium output and the price level?
Prob 20 16a. In the grid, graph the aggregate demand and short-run aggregate supply curves (label them AD0 and SRAS0). What are equilibrium output and the price level?Question
Assume aggregate demand grows by 100% (output doubles at each price level). Graph the new aggregate demand curve and label it AD1. What is the new equilibrium output and price level?
Prob 20 16b. Assume aggregate demand grows by 100% (output doubles at each price level). Graph the new aggregate demand curve and label it AD1. What is the new equilibrium output and price level?Question
If full employment output is 600, what will be the long-run output and price level given the new aggregate demand curve?
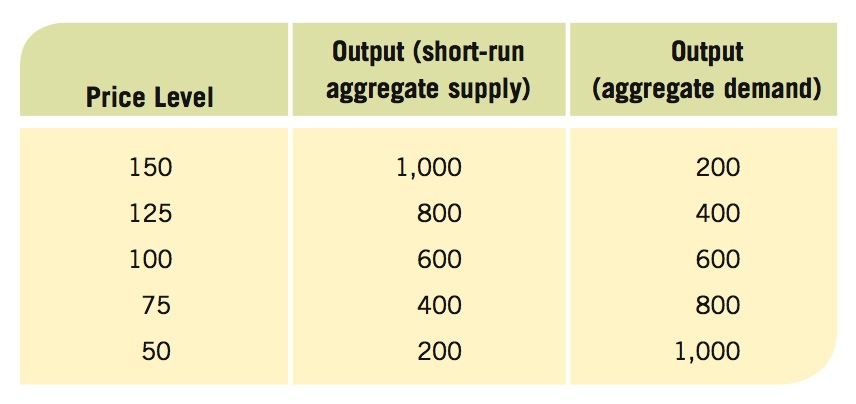
 Prob 20 16c. If full employment output is 600, what will be the long-run output and price level given the new aggregate demand curve?
Prob 20 16c. If full employment output is 600, what will be the long-run output and price level given the new aggregate demand curve?

Question
According to By the Numbers, if the average price of a barrel of oil is $100, and total aggregate demand in 2012 was $15 trillion in the United States and $9 trillion in China, what percentage of aggregate demand did oil consumption represent in each country?
Prob 20 17. According to By the Numbers, if the average price of a barrel of oil is $100, and total aggregate demand in 2012 was $15 trillion in the United States and $9 trillion in China, what percentage of aggregate demand did oil consumption represent in each country?When the economy is operating at full employment, why is an increase in aggregate demand not helpful to the economy?Question
According to By the Numbers, which state has the highest rate of home ownership? Which state has the lowest rate of home ownership? What are some reasons why these states represent the highest rate and lowest rate of home ownership?
Prob 20 18. According to By the Numbers, which state has the highest rate of home ownership? Which state has the lowest rate of home ownership? What are some reasons why these states represent the highest rate and lowest rate of home ownership?When the economy is operating at full employment, why is an increase in aggregate demand not helpful to the economy?