The Balance of Payments
All open economies have balance of payments accounts. Open financial markets permit economies to run trade surpluses and deficits.
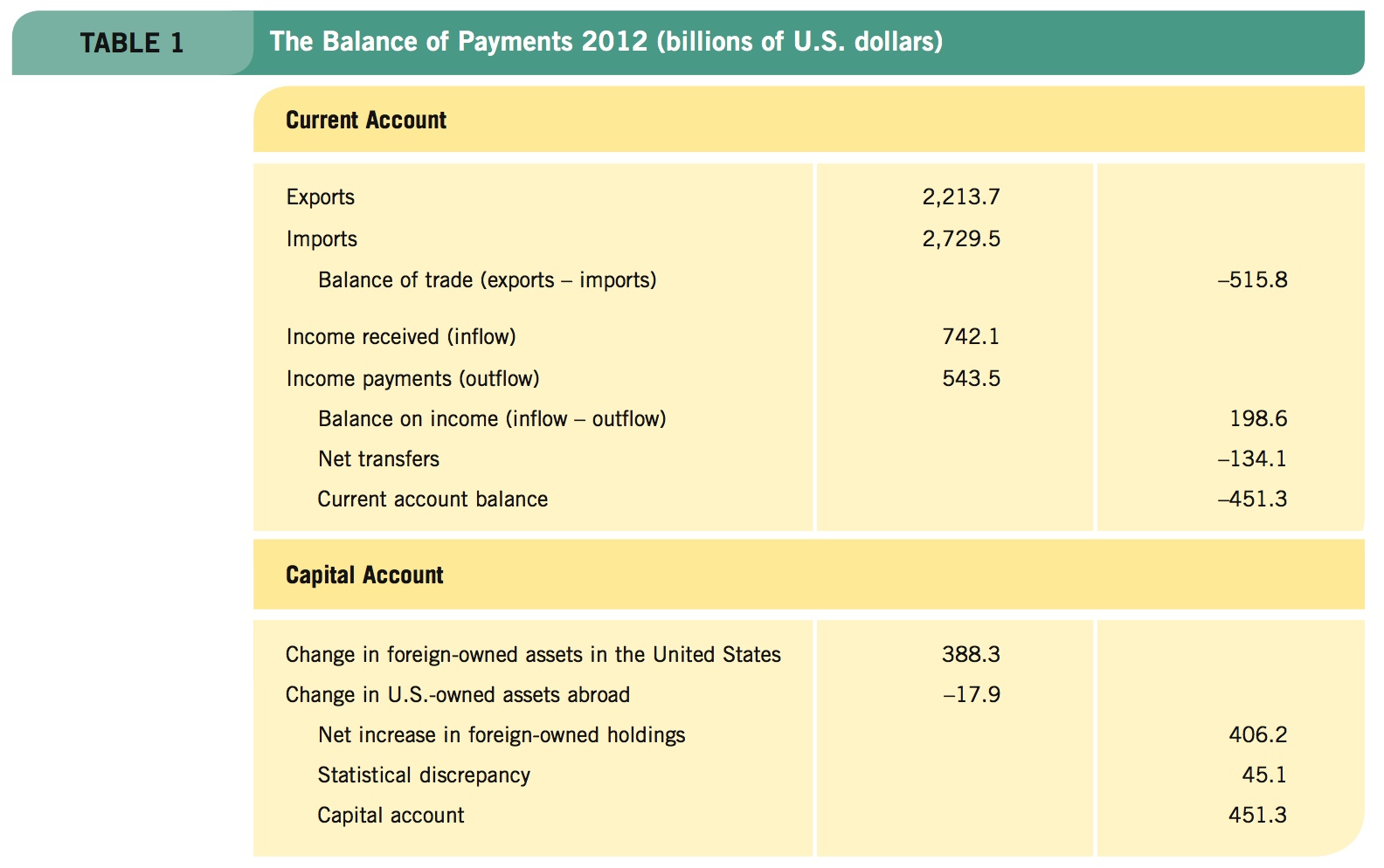
A simplified version of the U.S. balance of payments accounts for 2012 is shown in Table 1. These accounts were compiled by the Bureau of Economic Analysis of the U.S. Department of Commerce. The balance of payments represents all payments received from foreign countries and all payments made to them. Notice that the accounts are split into two broad divisions, the current account and the capital account.
The Current Account
current account Includes payments for imports and exports of goods and services, incomes flowing into and out of the country, and net transfers of money.
The current account includes payments for imports and exports of goods and services, incomes flowing into and out of the country, and net transfers of money.
Imports and Exports In 2012, U.S. exports of goods and services totaled $2,213.7 billion, with imports totaling $2,729.5 billion. This exchange produced a trade deficit of $515.8 billion because we imported more than we exported. Some balance of payments accounts break exports and imports into separate categories of goods and services; here they are combined. This component of the current account is known as the balance of trade.
399
The Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market is the world’s largest trading exchange, far surpassing the total value of all bond and stock transactions throughout the world. Currencies are traded 24 hours a day from Sunday 5 p.m. EST to Friday 5 p.m. EST in major foreign exchanges in London, Tokyo, New York, and Sydney.
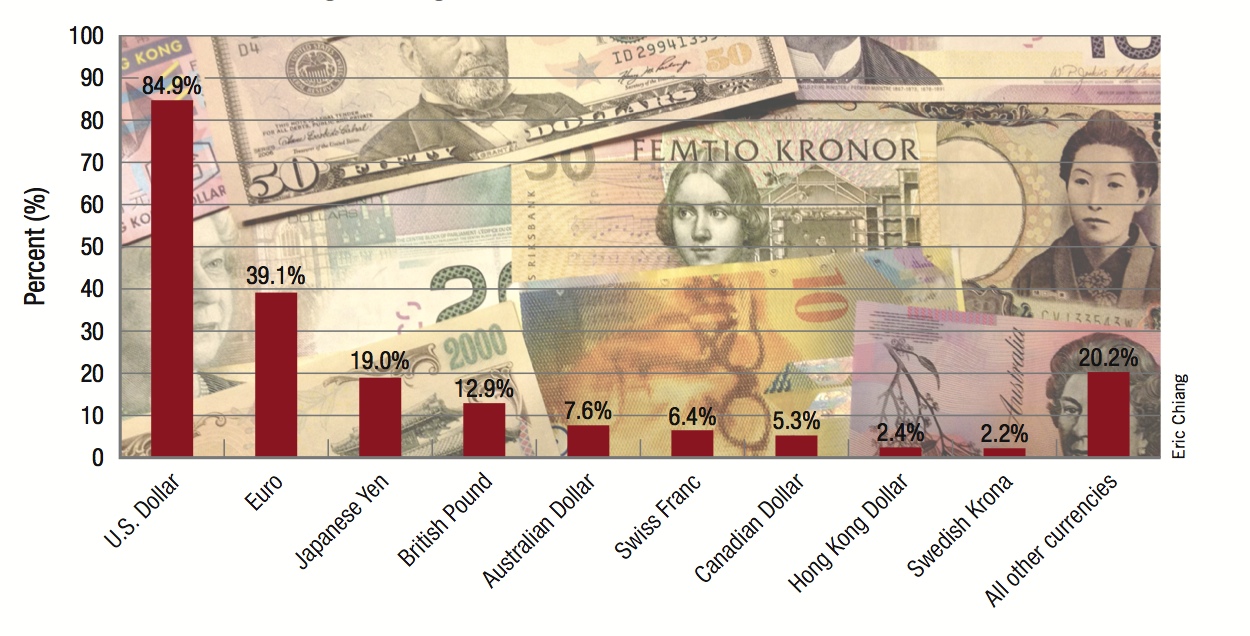
The most traded currencies in the world are shown. Because each transaction involves two currencies, the percentages add up to 200%. The U.S. dollar is involved in 84.9% of all foreign exchange transactions.


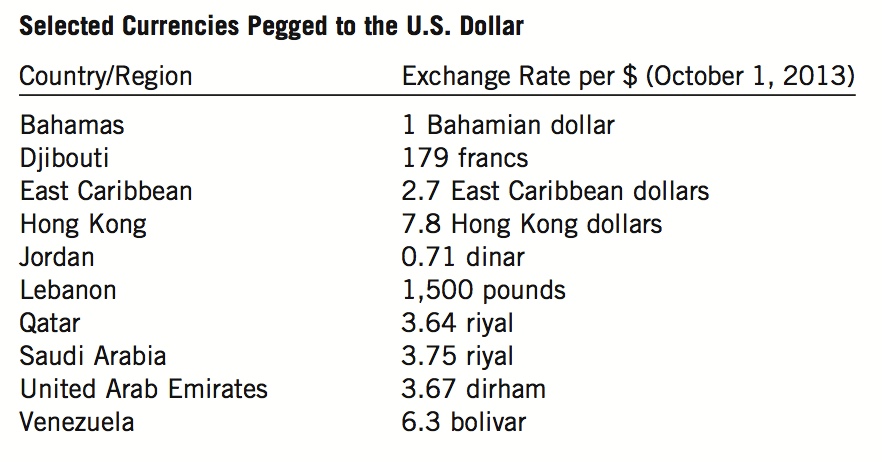
Approximately twenty nations peg their currencies (maintain a fixed exchange rate) to the U.S. dollar. Three nations (as of 2013)—Panama, Ecuador, and El Salvador—have gone even further, adopting the U.S. dollar as their official currency.
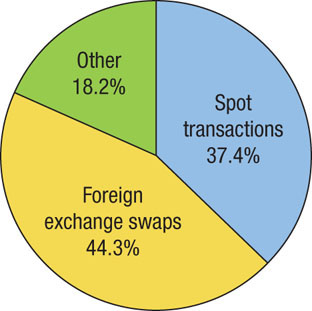
Foreign exchange swaps, or contracts to buy and sell a fixed amount of foreign currency on two different dates, are the most common type of foreign exchange transaction, followed by spot transactions, which are foreign currency trades at the current exchange rate. Together, these transactions comprise nearly 82% of all foreign exchange transactions. The remaining 18% includes other foreign exchange trades such as options and futures.
400
Income Another source of foreign payments to the United States comprises income flows, which include wages, rents, interest, and profits that Americans earn abroad ($742.1 billion in 2012) minus the corresponding income foreigners earn in the United States ($543.5 billion). On balance, foreigners earned $198.6 billion less in the United States than U.S. citizens and corporations earned abroad in 2012.
Transfers Direct transfers of money also take place between the United States and other countries. These transfers include foreign aid, funds sent to such international organizations as the United Nations, and stipends paid directly to foreign students studying in the United States or U.S. students studying abroad. These transfers also include the money that people working in the United States send back to their families in foreign countries. Net transfers for 2012 totaled −$134.1 billion.
Adding all current account categories for 2012 yields a current account deficit of $451.3 billion. In 2012, the United States paid out $451.3 billion more than it received. Therefore, the United States had to borrow $451.3 billion from the rest of the world, or the net holdings of U.S. assets by foreigners must have increased by that same amount, or some combination of the two.
The Capital Account
capital account Summarizes the flow of money into and out of domestic and foreign assets, including investments by foreign companies in domestic plants or subsidiaries, and other foreign holdings of U.S. assets, including mutual funds, stocks, bonds, and deposits in U.S. banks. Also included are U.S. investors’ holdings of foreign financial assets, production facilities, and other assets in foreign countries.

The capital account summarizes the flow of money into and out of domestic and foreign assets. This account includes investments by foreign companies in domestic plants or subsidiaries—a Toyota truck plant in Tennessee, for example. Note that the profits from such investments flow abroad, and thus they are in the income payments (outflow) category of the current account. Other foreign holdings of U.S. assets include portfolio investments such as mutual funds, stocks, bonds, and deposits in U.S. banks. American investors hold foreign financial assets in their portfolios, including foreign stocks and bonds. And American companies own plants and other assets in foreign countries.
401
Because the United States ran a current account deficit in 2012, it must run a capital account surplus. Net capital inflows into the United States must equal $451.3 billion to offset the current account deficit. Indeed, foreign-owned assets in the United States rose by $388.3 billion, while U.S. ownership of foreign assets actually fell by $17.9 billion (meaning that foreign investors bought back assets previously acquired by U.S. investors abroad), resulting in a net inflow of capital of $406.2 billion. Because many accounts are subjected to estimation errors, a statistical discrepancy value of $45.1 billion is added to the net inflow of capital to bring the total capital account surplus to $451.3 billion.
The key point to remember is that balance of payments accounts have to show a balance: A deficit in the current account must be offset by a corresponding surplus in the capital account, and vice versa. Keep this point in mind as we go on to look at foreign exchange and policy implications of an open economy.
THE BALANCE OF PAYMENTS
- The balance of payments represents all payments received from foreign countries and all payments made to them.
- The balance of payments is split into two categories: current and capital accounts.
- The current account includes payment for exports and imports, income flows, and net transfers of money.
- The capital account summarizes flows of money into and out of domestic and foreign assets.
- The sum of the current and capital account balances must equal zero.
QUESTION: China and Russia both have a high savings rate as a percent of GDP. The lack of consumption relative to domestic investment leads to substantial net exports. Would this situation lead to a current account surplus or a current account deficit? Why?
When a country has a high savings rate (relative to domestic investment), it is likely that its exports will exceed imports, resulting in a trade surplus. Both China and Russia are net exporters, which shows up as a current account surplus in their balance of payments accounts.