Questions and Problems
Check Your Understanding
Question
When can an economy increase the production of one good without reducing the output of another?
Prob 2 1. When can an economy increase the production of one good without reducing the output of another?Question
In which of the three basic questions facing any society does technology play the greatest role?
Prob 2 2. In which of the three basic questions facing any society does technology play the greatest role?Question
Explain the important difference between a straight line PPF and the PPF that is concave to (bowed away from) the origin.
Prob 2 3. Explain the important difference between a straight line PPF and the PPF that is concave to (bowed away from) the origin.Question
How would unemployment be shown on the PPF?
Prob 2 4. How would unemployment be shown on the PPF?Question
List three factors that can contribute to an economy’s growth.
Prob 2 5. List three factors that can contribute to an economy’s growth.Question
How can a country that does not have an absolute advantage in producing goods still benefit from trade?
Prob 2 6. How can a country that does not have an absolute advantage in producing goods still benefit from trade?
Apply the Concepts
Question
China has experienced levels of economic growth in the last decade that have been about 5 times that of the United States (10% versus 2% per year in the United States). Has China’s high growth rate eliminated scarcity in China?
Prob 2 7. China has experienced levels of economic growth in the last decade that have been about 5 times that of the United States (10% versus 2% per year in the United States). Has China’s high growth rate eliminated scarcity in China?Question
Describe how a country producing more capital goods rather than consumption goods ends up in the future with a PPF that is larger than a country that produces more consumption goods and fewer capital goods.
Prob 2 8. Describe how a country producing more capital goods rather than consumption goods ends up in the future with a PPF that is larger than a country that produces more consumption goods and fewer capital goods.Question
The United States has an absolute advantage in making many goods, such as shortsleeved cotton golf shirts. Why do Indonesia and Bangladesh make these shirts and export them to the United States?
Prob 2 9. The United States has an absolute advantage in making many goods, such as shortsleeved cotton golf shirts. Why do Indonesia and Bangladesh make these shirts and export them to the United States?Question
Why is it that America uses heavy street cleaning machines driven by one person to clean the streets, while China and India use many people with brooms to do the same job?
Prob 2 10. Why is it that America uses heavy street cleaning machines driven by one person to clean the streets, while China and India use many people with brooms to do the same job?Question
If specialization and trade as discussed in this chapter lead to a win-win situation in which both countries gain, why is there often opposition to trade agreements and globalization?
Prob 2 11. If specialization and trade as discussed in this chapter lead to a win-win situation in which both countries gain, why is there often opposition to trade agreements and globalization?Question
American attitudes about the tradeoff between the environment and economic growth shown in By the Numbers at the beginning of the chapter changed significantly when the economy entered a recession. However, during the recession in 2009, Americans were roughly equally split between their concerns for the environment and economic growth. What would you expect to find in a similar survey in a relatively poor developing nation?
Prob 2 12. American attitudes about the tradeoff between the environment and economic growth shown in By the Numbers at the beginning of the chapter changed significantly when the economy entered a recession. However, during the recession in 2009, Americans were roughly equally split between their concerns for the environment and economic growth. What would you expect to find in a similar survey in a relatively poor developing nation?
In the News
Question
According to a March 8, 2012, New York Times report, the 2011 earthquake in Japan that triggered a devastating tsunami led to a near complete shutdown of Japan’s nuclear energy industry, which generates one-third of the country’s total electricity. The resulting energy crisis caused severe supply disruptions in nearly all industries. How do natural disasters such as the tsunami in Japan affect a country’s ability to achieve economic growth? Illustrate your answer using a PPF.
Prob 2 13. According to a March 8, 2012, New York Times report, the 2011 earthquake in Japan that triggered a devastating tsunami led to a near complete shutdown of Japan’s nuclear energy industry, which generates one-third of the country’s total electricity. The resulting energy crisis caused severe supply disruptions in nearly all industries. How do natural disasters such as the tsunami in Japan affect a country’s ability to achieve economic growth? Illustrate your answer using a PPF.Question
The recession of 2007–2009 and the slow recovery led to severe budget cuts in state governments across the United States. Public colleges and universities, which are highly subsidized by state governments, saw dramatic cuts in their budgets, making it more difficult for students to attend school and/or complete their degrees. The Chronicle of Higher Education of January 17, 2012, argued that cuts to higher education will “imperil competitiveness” in America. How might the cost savings from reduced educational spending end up costing states even more in the future?
Prob 2 14. The recession of 2007–2009 and the slow recovery led to severe budget cuts in state governments across the United States. Public colleges and universities, which are highly subsidized by state governments, saw dramatic cuts in their budgets, making it more difficult for students to attend school and/or complete their degrees. The Chronicle of Higher Education of January 17, 2012, argued that cuts to higher education will “imperil competitiveness” in America. How might the cost savings from reduced educational spending end up costing states even more in the future?
Solving Problems
Question
Political commentators often make the argument that growth in another country (most notably China) is detrimental to the economic interests of the United States. Look back at Tables 2 to 4 in the Gains from Trade section of the chapter. Then, assume that Mexico doubles in size, and make those changes to Table 2. Reconstruct Tables 3 and 4 given Mexico’s greater capacity. Has the United States benefited by Mexico being able to produce more?
Prob 2 15. Political commentators often make the argument that growth in another country (most notably China) is detrimental to the economic interests of the United States. Look back at Tables 2 to 4 in the Gains from Trade section of the chapter. Then, assume that Mexico doubles in size, and make those changes to Table 2. Reconstruct Tables 3 and 4 given Mexico’s greater capacity. Has the United States benefited by Mexico being able to produce more?- The table below shows the potential output combinations of oranges and jars of prickly pear jelly (from the flower of the prickly pear cactus) for Florida and Arizona.
Question
Compute the opportunity cost for Florida of oranges in terms of jars of prickly pear jelly. Do the same for prickly pear jelly in terms of oranges.
Prob 2 16a. Compute the opportunity cost for Florida of oranges in terms of jars of prickly pear jelly. Do the same for prickly pear jelly in terms of oranges.Question
Compute the opportunity cost for Arizona of oranges in terms of jars of prickly pear jelly. Do the same for prickly pear jelly in terms of oranges.
Prob 2 16b. Compute the opportunity cost for Arizona of oranges in terms of jars of prickly pear jelly. Do the same for prickly pear jelly in terms of oranges.Question
Would it make sense for Florida to specialize in producing oranges and for Arizona to specialize in producing prickly pear jelly and then trade? Why or why not?
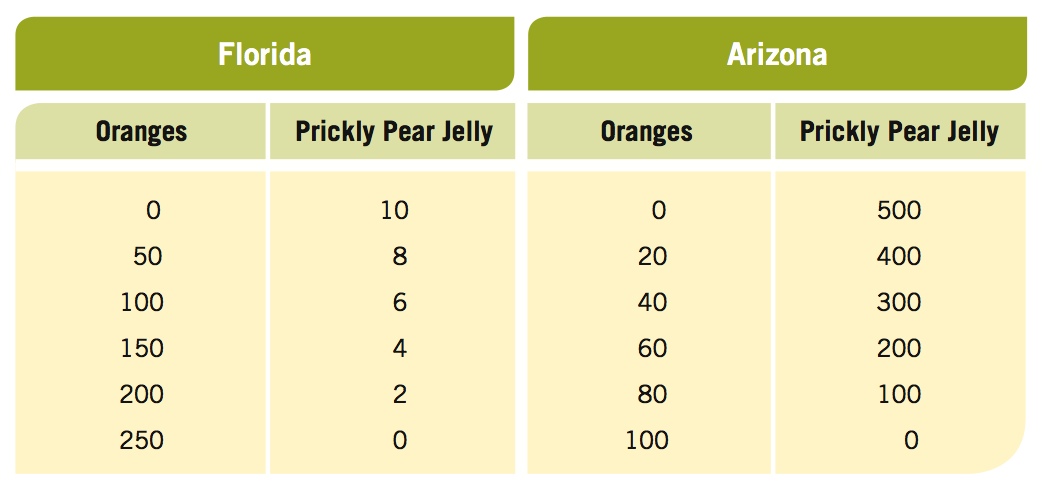 Prob 2 16c. Would it make sense for Florida to specialize in producing oranges and for Arizona to specialize in producing prickly pear jelly and then trade? Why or why not?
Prob 2 16c. Would it make sense for Florida to specialize in producing oranges and for Arizona to specialize in producing prickly pear jelly and then trade? Why or why not?

Question
According to By the Numbers, in which period (1960 to 1985 or 1985 to 2010) did corn and soybean production increase faster in terms of yield per acre?
Prob 2 17. According to By the Numbers, in which period (1960 to 1985 or 1985 to 2010) did corn and soybean production increase faster in terms of yield per acre?Question
According to By the Numbers, in the period between 1990 and 2012, in how many years did the U.S. trade balance improve from the previous year and in how many years did the trade balance deteriorate (assume the trade balance deteriorated from 1989 [not shown in the figure] to 1990)?
Prob 2 18. According to By the Numbers, in the period between 1990 and 2012, in how many years did the U.S. trade balance improve from the previous year and in how many years did the trade balance deteriorate (assume the trade balance deteriorated from 1989 [not shown in the figure] to 1990)?