Questions and Problems
Check Your Understanding
Question
Product prices give consumers and businesses a lot of information besides just the price. What kinds of information?
Prob 3 1. Product prices give consumers and businesses a lot of information besides just the price. What kinds of information?Question
Describe the determinants of demand. Why are they important?
Prob 3 2. Describe the determinants of demand. Why are they important?Question
As the world population ages, will the demand for cholesterol drugs increase, decrease, or remain the same? Assume there is a positive relationship between aging and cholesterol levels. Would this cause a change in demand or a change in quantity demanded?
Prob 3 3. As the world population ages, will the demand for cholesterol drugs increase, decrease, or remain the same? Assume there is a positive relationship between aging and cholesterol levels. Would this cause a change in demand or a change in quantity demanded?Question
Describe some of the reasons why supply changes. Improved technology typically results in lower prices for most products. Why do you think this is true? Describe the difference between a change in supply and a change in quantity supplied.
Prob 3 4. Describe some of the reasons why supply changes. Improved technology typically results in lower prices for most products. Why do you think this is true? Describe the difference between a change in supply and a change in quantity supplied.Question
If a strong economic recovery boosts average incomes, what would happen to the equilibrium price and quantity for a normal good? How about an inferior good?
Prob 3 5. If a strong economic recovery boosts average incomes, what would happen to the equilibrium price and quantity for a normal good? How about an inferior good?Question
Suppose the market for tomatoes is in equilibrium, and events occur that simultaneously shift both the demand and supply curves to the right. Is it possible to determine how the equilibrium price and/or quantity would change?
Prob 3 6. Suppose the market for tomatoes is in equilibrium, and events occur that simultaneously shift both the demand and supply curves to the right. Is it possible to determine how the equilibrium price and/or quantity would change?
Apply the Concepts
Question
Demand for tickets to sporting events such as the Super Bowl has increased. Has supply increased? What does the answer to this tell you about the price of these tickets compared to prices a few years ago?
Prob 3 7. Demand for tickets to sporting events such as the Super Bowl has increased. Has supply increased? What does the answer to this tell you about the price of these tickets compared to prices a few years ago?Question
Suppose the price of monthly data plans required to access the Internet anywhere using a tablet computer falls in price. How would this affect the market for tablet computers?
Prob 3 8. Suppose the price of monthly data plans required to access the Internet anywhere using a tablet computer falls in price. How would this affect the market for tablet computers?- Using the figures, answer the following questions:
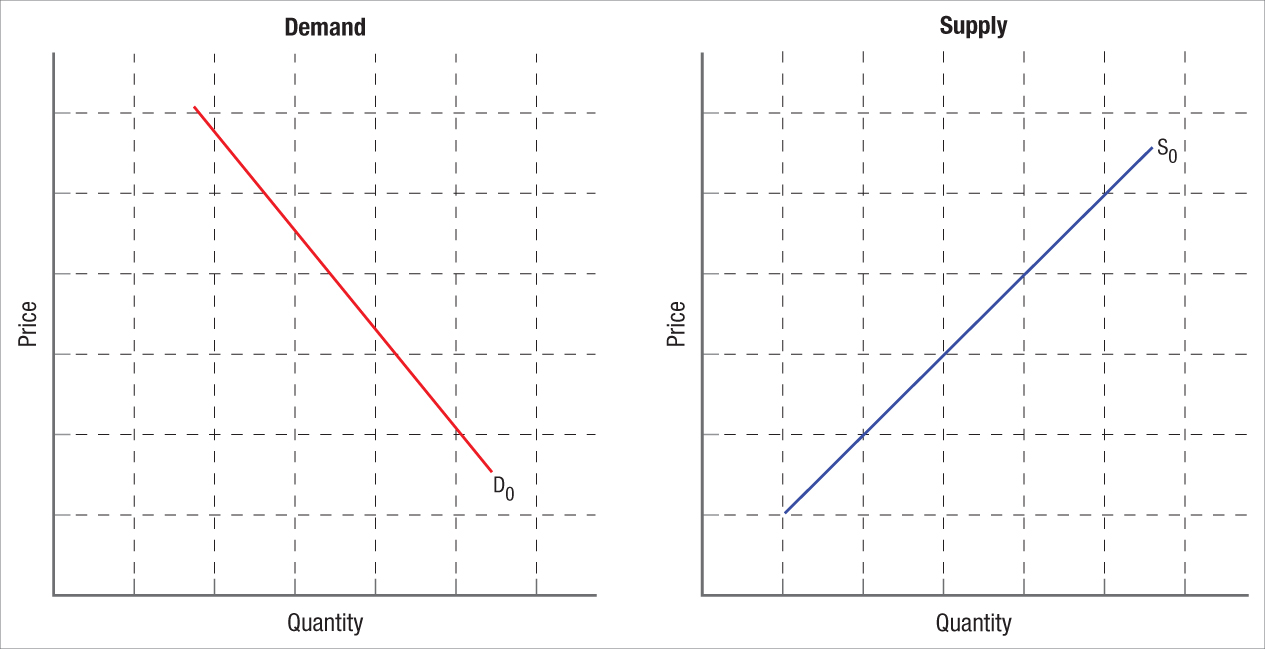
Question
On the Demand panel:
Show a decrease in demand and label it D2.
Show an increase in quantity demanded.
Show a decrease in quantity demanded.
What causes demand to change?
What causes quantity demanded to change?Prob 3 9a. On the Demand panel: Show a decrease in demand and label it D2. Show an increase in quantity demanded. Show a decrease in quantity demanded. What causes demand to change? What causes quantity demanded to change?Question
On the Supply panel:
Show an increase in supply and label it S1.
Show a decrease in supply and label it S2.
Show an increase in quantity supplied.
What causes supply to change?
What causes quantity supplied to change?Prob 3 9b. On the Supply panel: Show an increase in supply and label it S1. Show a decrease in supply and label it S2. Show an increase in quantity supplied. What causes supply to change? What causes quantity supplied to change?
Question
Several medical studies have shown that drinking red wine in moderation is good for the heart. How would such a study affect the public’s demand for wine? Would it have an impact on the type of grapes planted in new vineyards?
Prob 3 10. Several medical studies have shown that drinking red wine in moderation is good for the heart. How would such a study affect the public’s demand for wine? Would it have an impact on the type of grapes planted in new vineyards?Question
Assume initially that the demand and supply for premium coffees (one-pound bags) are in equilibrium. Now assume Starbucks introduces the world to premium blends, and so demand rises substantially. Describe what will happen in this market as it moves to a new equilibrium. If a hard freeze eliminates Brazil’s premium coffee crop, what will happen to the price of premium coffee?
Prob 3 11. Assume initially that the demand and supply for premium coffees (one-pound bags) are in equilibrium. Now assume Starbucks introduces the world to premium blends, and so demand rises substantially. Describe what will happen in this market as it moves to a new equilibrium. If a hard freeze eliminates Brazil’s premium coffee crop, what will happen to the price of premium coffee?Question
Over the past decade, cruise ship companies have dramatically increased the number of mega-ships (those that carry 3,000 passengers or more), increasing the supply of cruises. At the same time, the popularity of cruising has increased among consumers, increasing demand. Explain how these two effects can coincide with a decrease in the average price of cruise travel.
Prob 3 12. Over the past decade, cruise ship companies have dramatically increased the number of mega-ships (those that carry 3,000 passengers or more), increasing the supply of cruises. At the same time, the popularity of cruising has increased among consumers, increasing demand. Explain how these two effects can coincide with a decrease in the average price of cruise travel.
In the News
Question
In China, a small but increasing number of people are choosing to work as professional queuers, and exactly as it sounds, they are paid to wait in line for others. An NPR story in July 25, 2011, tells the story of a few professional queuers who earn about $3 an hour to wait in line, a wage that is about double that of the typical factory worker in China. Given that one can easily pay someone else to wait, what do you think will happen in the market for goods and services most prone to long waiting times, such as for concert tickets, the latest technology gadget, or low-cost apartments?
Prob 3 13. In China, a small but increasing number of people are choosing to work as professional queuers, and exactly as it sounds, they are paid to wait in line for others. An NPR story in July 25, 2011, tells the story of a few professional queuers who earn about $3 an hour to wait in line, a wage that is about double that of the typical factory worker in China. Given that one can easily pay someone else to wait, what do you think will happen in the market for goods and services most prone to long waiting times, such as for concert tickets, the latest technology gadget, or low-cost apartments?Question
An August 12, 2011, article in Time Magazine, “As Regular Malls Struggle, Outlet Malls Are Booming,” analyzed trends in how consumers shop, and found that more and more consumers are visiting outlet malls as a way to save money on name brand clothing and housewares. Given that most stores offer an outlet option, why would anyone choose to pay more at regular malls? Use supply and demand analysis to explain why prices differ between regular stores and outlet stores. Why would outlet stores be a strategic way for businesses to sell their unsold (surplus) goods instead of just offering a sale at their regular stores?
Prob 3 14. An August 12, 2011, article in Time Magazine, “As Regular Malls Struggle, Outlet Malls Are Booming,” analyzed trends in how consumers shop, and found that more and more consumers are visiting outlet malls as a way to save money on name brand clothing and housewares. Given that most stores offer an outlet option, why would anyone choose to pay more at regular malls? Use supply and demand analysis to explain why prices differ between regular stores and outlet stores. Why would outlet stores be a strategic way for businesses to sell their unsold (surplus) goods instead of just offering a sale at their regular stores?
Solving Problems
- The table below represents the world supply and demand for natural vanilla in thousands of pounds. A large portion of natural vanilla is grown in Madagascar and comes from orchids that require a lot of time to cultivate. The sequence of events described below actually happened, but the numbers have been altered to make the calculations easier. (See James Altucher, “Supply, Demand, and Edible Orchids,” Financial Times, September 20, 2005, p. 12.) Assume the original supply and demand curves are represented in the table below.
Price ($/pound) Quantity Demanded (thousands) Quantity Supplied (thousands) 0 20 0 10 16 6 20 12 12 30 8 18 40 4 24 50 0 30 Question
Graph both the supply (S0) and demand (D0) curves. What is the current equilibrium price? Label that point a.
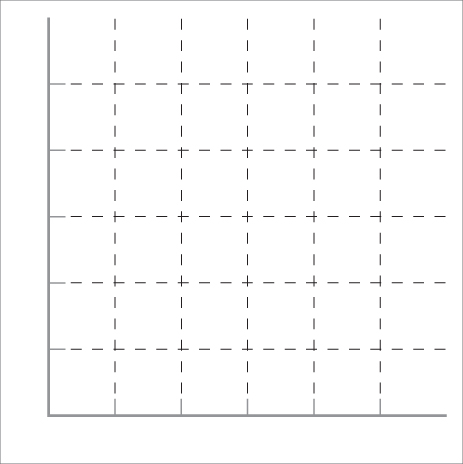 Prob 3 15a. Graph both the supply (S0) and demand (D0) curves. What is the current equilibrium price? Label that point a.
Prob 3 15a. Graph both the supply (S0) and demand (D0) curves. What is the current equilibrium price? Label that point a.Question
Assume that Madagascar is hit by a hurricane (which actually did happen in 2000), and the world’s supply of vanilla is reduced by five-sixths, or 83%. Label the new supply curve (S1). What will be the new equilibrium price in the market? Label that point b.
Prob 3 15b. Assume that Madagascar is hit by a hurricane (which actually did happen in 2000), and the world’s supply of vanilla is reduced by five-sixths, or 83%. Label the new supply curve (S1). What will be the new equilibrium price in the market? Label that point b.Question
Now assume that Coca-Cola announces plans to introduce a new “Vanilla Coke,” and this increases the demand for natural vanilla by 25%. Label the new demand curve (D1). What will be the new equilibrium price? Label this new equilibrium point c. Remember that the supply of natural vanilla was reduced by the hurricane earlier.
Prob 3 15c. Now assume that Coca-Cola announces plans to introduce a new “Vanilla Coke,” and this increases the demand for natural vanilla by 25%. Label the new demand curve (D1). What will be the new equilibrium price? Label this new equilibrium point c. Remember that the supply of natural vanilla was reduced by the hurricane earlier.Question
Growing the orchids that produce natural vanilla requires a climate with roughly 80% humidity, and the possible grower countries generally fall within 20° north or south of the equator. A doubling of prices encouraged several other countries (e.g., Uganda and Indonesia) to begin growing orchids or increase their current production. Within several years, supply was back to normal (S0), but by then, synthetic vanilla had replaced 80% of the original demand (D0). Label this new demand curve (D2). What is the new equilibrium price and output?
Prob 3 15d. Now assume that Coca-Cola announces plans to introduce a new “Vanilla Coke,” and this increases the demand for natural vanilla by 25%. Label the new demand curve (D1). What will be the new equilibrium price? Label this new equilibrium point c. Remember that the supply of natural vanilla was reduced by the hurricane earlier.
- The following figure shows the supply and demand for strawberries. Answer the questions that follow.
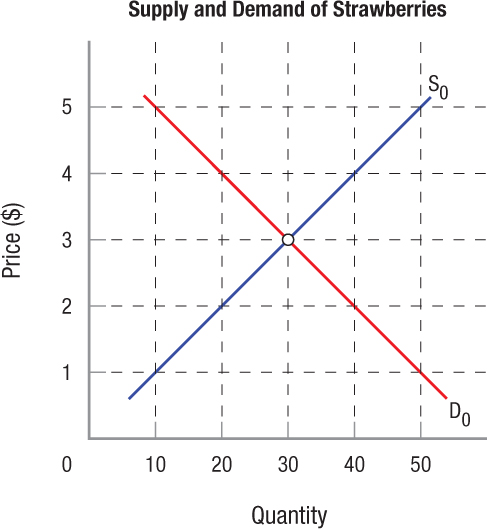
Question
Indicate the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity.
Prob 3 16a. Indicate the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity.Question
Suppose sellers try to sell strawberries at $4. How much of a shortage or a surplus of strawberries would result?
Prob 3 16b. Suppose sellers try to sell strawberries at $4. How much of a shortage or a surplus of strawberries would result?Question
Now suppose that the demand for strawberries falls by ten units at every price. Draw the new demand curve in the figure, and estimate what the new equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity would be.
Prob 3 16c. Now suppose that the demand for strawberries falls by ten units at every price. Draw the new demand curve in the figure, and estimate what the new equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity would be.Question
If sellers still try to sell strawberries at $4, would the shortage or the surplus increase or decrease?
Prob 3 16d. If sellers still try to sell strawberries at $4, would the shortage or the surplus increase or decrease?

Question
According to By the Numbers, about how many times larger is the bottled water market in the United States in the year 2012 compared to 1982?
Prob 3 17. According to By the Numbers, about how many times larger is the bottled water market in the United States in the year 2012 compared to 1982?Question
According to By the Numbers, which of the following categories of college/university enrollment have risen from 1996 to 2012: public two year, public four year, private not-for-profit, private for-profit? Which of these categories have fallen in enrollment from 1996 to 2012?
Prob 3 18. According to By the Numbers, which of the following categories of college/university enrollment have risen from 1996 to 2012: public two year, public four year, private not-for-profit, private for-profit? Which of these categories have fallen in enrollment from 1996 to 2012?