Chapter Summary
Chapter Summary
Section 1: Elasticity of Demand
The price elasticity of demand measures how sensitive consumers are to changes in price.
What Do the ED Numbers Mean?
ED > 1: Elastic Demand (many substitutes, high-priced goods, longer time horizon, luxury goods)
ED < 1: Inelastic Demand (few substitutes, low-priced goods, shorter time horizon, necessities)
ED = 1: Unitary Elastic Demand (a change in price results in an equal % change in quantity demanded)

The formula for price elasticity of demand is:
ED = % change in quantity demanded /% change in price
Since all ED must be negative according to the law of demand, the convention is to drop the negative sign.
Calculating % changes: base method versus midpoint method base method: % Δ in P = Δ in P/old P
The base method is simple because it is how one normally calculates percentages in everyday life, such as for store discounts or restaurant tips. For example, adding a 15% tip to a $20 bill is $3, or taking 25% off of a $40 shirt makes the shirt $30 using the base method.

midpoint method: % Δ in P = Δ in P/[(old P + new P)/2] The midpoint method is slightly more difficult to calculate; however, the advantage is that the percentage change stays the same whether a value increases or decreases. For example, using the midpoint method, going from 10 to 20 or from 20 to 10 is a 66.7% change in either direction.
How Do You Remember Which Diagram Is Elastic?
Think of a pair of shorts: You can easily pull them side-to-side because the waistband is very elastic!
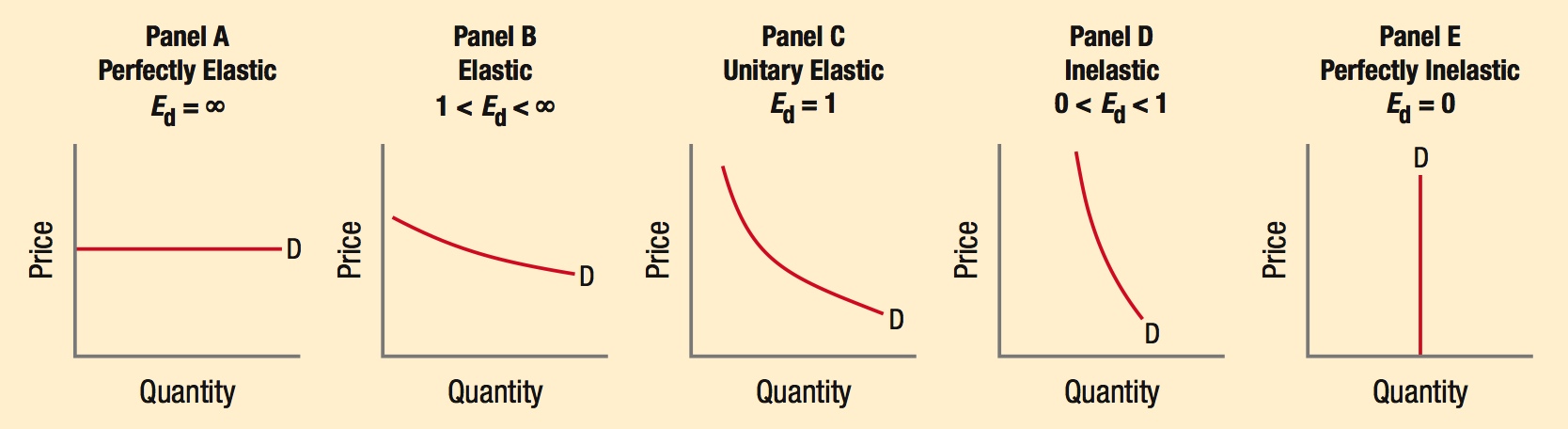
The flatter the demand curve, the more elastic the good or service; the steeper the demand curve, the more inelastic the good or service. Because elasticity changes along a linear demand curve, unitary elastic demand has a curved shape.
Section 2: Total Revenue and Other Measures of Elasticity
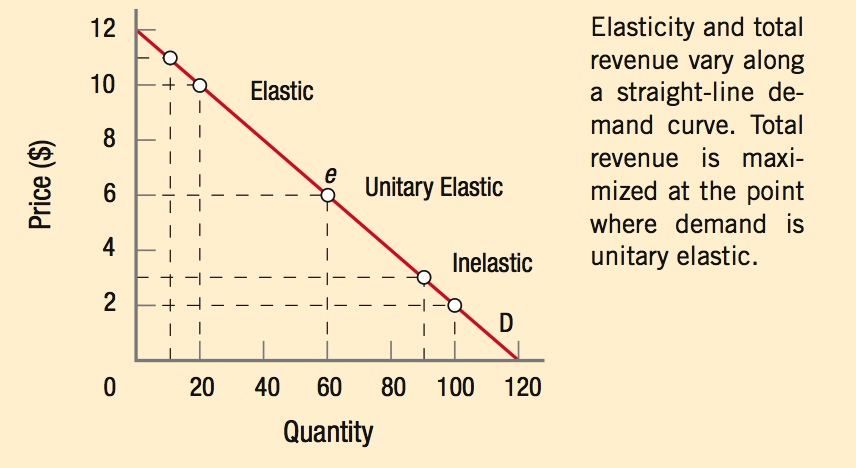
Total revenue is calculated as price × quantity demanded.
Total revenue increases when price rises on an inelastic good or is lowered on an elastic good.
Total revenue decreases when price rises on an elastic good or is lowered on an inelastic good.

Income elasticity of demand measures how quantity demand responds to changes in income: EY = %Δ Q/%ΔIncome
0 < EY < 1: normal good
EY > 1: luxury good
EY < 0: inferior good
Cross elasticity of demand measures how responsive quantity demand for one good is to a change in the price of another good: Eab = % ΔQa /% ΔPb
Eab > 0: Goods a and b are substitutes
Eab < 0: Goods a and b are complements
Eab = 0: Goods a and b are unrelated
Section 3: Elasticity of Supply
The elasticity of supply measures the extent to which businesses react to price changes.
The elasticity of supply formula is virtually identical to that of demand:
ES = %ΔQuantity Supplied / %ΔPrice
The base and midpoint methods both are still used to calculate % changes.
The time horizon affects the elasticity of supply: the longer the period, the more a firm is able to adjust to changing prices, and therefore the more elastic the good.
Short run: a time period in which plant capacity is fixed and the number of firms in an industry does not change.
Long run: a time period long enough for firms to alter their plant capacity or for firms to enter or leave the industry.
Section 4: Taxes and Elasticity
The incidence of taxation refers to who bears the economic burden of a tax.
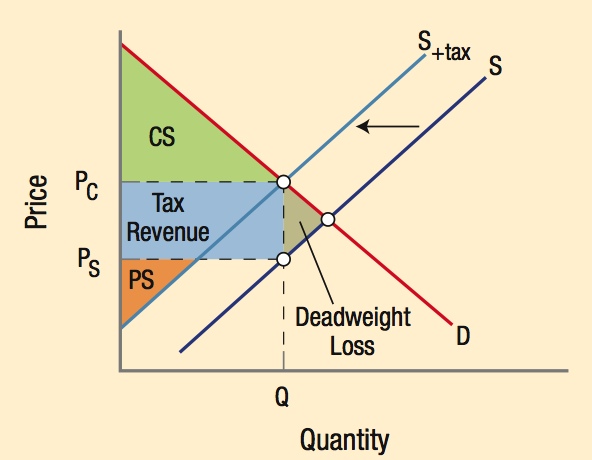
The more elastic the demand or inelastic the supply, the greater the incidence of a tax on sellers. The more inelastic the demand or elastic the supply, the greater the incidence of a tax on consumers.
The tax created a deadweight loss shown in gray, along with a reduction in consumer surplus (CS) and producer surplus (PS). The government collects tax revenue shown as the area in blue.
A new tax collected on sellers shifts the supply curve to the left. The intersection of S+ tax and D is the price consumers pay, PC. PS is the price sellers receive. The difference between PC and PS is the tax per unit.