Questions and Problems
Check Your Understanding
Question
What is the difference between explicit and implicit costs? What is the difference between economic and accounting profits? Are these four concepts related? How?
Prob 7 1. What is the difference between explicit and implicit costs? What is the difference between economic and accounting profits? Are these four concepts related? How?Question
Why should sunk costs be ignored for decision making?
Prob 7 2. Why should sunk costs be ignored for decision making?Question
How does the short run differ from the long run? Is the long run the same for all industries? Why or why not?
Prob 7 3. How does the short run differ from the long run? Is the long run the same for all industries? Why or why not?Question
Why should a firm never hire a worker when negative marginal returns set in?
Prob 7 4. Why should a firm never hire a worker when negative marginal returns set in?Question
Why is the average fixed cost curve not U-shaped? Why does it not turn up as the average variable cost and average total cost curves do?
Prob 7 5. Why is the average fixed cost curve not U-shaped? Why does it not turn up as the average variable cost and average total cost curves do?Question
What is the difference between marginal cost and average total cost?
Prob 7 6. What is the difference between marginal cost and average total cost?
Apply the Concepts
Question
If you work hard building your business and end up earning zero economic profit for the year, would this be considered a failed business to an economist? Why or why not?
Prob 7 7. If you work hard building your business and end up earning zero economic profit for the year, would this be considered a failed business to an economist? Why or why not?Question
In order to take this class, you had to pay tuition, buy the textbook, and buy a new laptop. Which of these items (if any) would be considered a sunk cost? Explain your reasoning.
Prob 7 8. In order to take this class, you had to pay tuition, buy the textbook, and buy a new laptop. Which of these items (if any) would be considered a sunk cost? Explain your reasoning.Question
Skype, the Internet phone company, uses peer-to-peer network principles to enable people to make free phone calls over the Internet to anywhere in the world. Skype forwards calls through users’ computers without having any central infrastructure. Users agree to let their computer’s excess capacity be used as transfer nodes. In this way, Skype does not have to invest in more infrastructure as it adds users, and the system is highly robust and scalable. What is the marginal cost to Skype to add another user to its system?
Prob 7 9. Skype, the Internet phone company, uses peer-to-peer network principles to enable people to make free phone calls over the Internet to anywhere in the world. Skype forwards calls through users’ computers without having any central infrastructure. Users agree to let their computer’s excess capacity be used as transfer nodes. In this way, Skype does not have to invest in more infrastructure as it adds users, and the system is highly robust and scalable. What is the marginal cost to Skype to add another user to its system?Question
List some of the reasons why the long-run average total cost curve has sort of a flat bowl shape. It declines early on, then is rather flat over a portion, and finally slopes upward.
Prob 7 10. List some of the reasons why the long-run average total cost curve has sort of a flat bowl shape. It declines early on, then is rather flat over a portion, and finally slopes upward.- The Finger Lakes region in New York State produces wine. The climate favors white wines, but reds have been produced successfully in the past 15 years. Categorize the following costs incurred by one winery as either fixed or variable:
Question
the capital used to buy 60 acres of land on Lake Seneca
Prob 7 11a. the capital used to buy 60 acres of land on Lake SenecaQuestion
the machine used to pick some varieties of grapes at the end of August and the beginning of September
Prob 7 11b. the machine used to pick some varieties of grapes at the end of August and the beginning of SeptemberQuestion
the salary of the chief vintner, who is employed year-round
Prob 7 11c. the salary of the chief vintner, who is employed year-roundQuestion
the wages paid to workers who bind the grape plants, usually in April, and usually over a period of three to four days
Prob 7 11d. the wages paid to workers who bind the grape plants, usually in April, and usually over a period of three to four daysQuestion
the wages paid to the same workers who pick the grapes at the end of August or early September
Prob 7 11e. the wages paid to the same workers who pick the grapes at the end of August or early SeptemberQuestion
the costs of the chemicals sprayed on the grapes in July
Prob 7 11f. the costs of the chemicals sprayed on the grapes in JulyQuestion
the wages of the wine expert who blends the wine in August and September, after the grapes have been picked
Prob 7 11g. the wages of the wine expert who blends the wine in August and September, after the grapes have been picked
Question
If marginal cost is less than average total cost, are average total costs rising or falling? Alternatively, if marginal cost is more than average total cost, are average total costs rising or falling? Explain how this example might apply to a basketball player attempting to achieve a high average points per game.
Prob 7 12. If marginal cost is less than average total cost, are average total costs rising or falling? Alternatively, if marginal cost is more than average total cost, are average total costs rising or falling? Explain how this example might apply to a basketball player attempting to achieve a high average points per game.
In the News
Question
Twenty-five years ago, coffee was a commodity product. Coffee brands such as Maxwell House (“good to the last drop”) and Folger’s advertised on television, but the difference between the brands was minimal. Not very satisfying, but no great pressure for change, either. In the 1990s, after touring coffeehouses in Rome, Howard Schultz brought the concept of upscale coffee to the United States and Starbucks was born (“Starbucks to Open 1,500 More Cafes in the U.S.,” The Seattle Times, December 5, 2012). In 2012, over 13,000 Starbucks existed in the United States alone. How could a company such as Starbucks make any money in a highly competitive market like coffee? What factors did Howard Schultz need to consider before venturing into this business?
Prob 7 13. Twenty-five years ago, coffee was a commodity product. Coffee brands such as Maxwell House (“good to the last drop”) and Folger’s advertised on television, but the difference between the brands was minimal. Not very satisfying, but no great pressure for change, either. In the 1990s, after touring coffeehouses in Rome, Howard Schultz brought the concept of upscale coffee to the United States and Starbucks was born (“Starbucks to Open 1,500 More Cafes in the U.S.,” The Seattle Times, December 5, 2012). In 2012, over 13,000 Starbucks existed in the United States alone. How could a company such as Starbucks make any money in a highly competitive market like coffee? What factors did Howard Schultz need to consider before venturing into this business?Question
When J. P. Morgan Chase, one of the largest banks in the world, admitted to an embarrassing $9 billion trading loss in 2012, policymakers rushed to propose new regulations to prevent banks from taking risky bets (“J. P. Morgan Loss Spurs Scrutiny of Fed Governance,” Wall Street Journal, May 14, 2012). Clearly, memories of bank bailouts by taxpayers in 2008 made the sentiment stronger. How do new regulations affect the costs of doing business? Do regulations represent a fixed or variable cost?
Prob 7 14. When J. P. Morgan Chase, one of the largest banks in the world, admitted to an embarrassing $9 billion trading loss in 2012, policymakers rushed to propose new regulations to prevent banks from taking risky bets (“J. P. Morgan Loss Spurs Scrutiny of Fed Governance,” Wall Street Journal, May 14, 2012). Clearly, memories of bank bailouts by taxpayers in 2008 made the sentiment stronger. How do new regulations affect the costs of doing business? Do regulations represent a fixed or variable cost?
Solving Problems
Question
Suppose you pay $10 to watch a movie at the local cineplex, and afterward you sneak into the next theater to watch a second movie without paying. What is your marginal cost of watching the second movie? What is the average cost of watching the two movies? After the movies, you go to the batting cages and stand in for two rounds of pitches, each round costing $2. What is your marginal cost of batting the second round? What is the average cost of batting two rounds?
Prob 7 15. Suppose you pay $10 to watch a movie at the local cineplex, and afterward you sneak into the next theater to watch a second movie without paying. What is your marginal cost of watching the second movie? What is the average cost of watching the two movies? After the movies, you go to the batting cages and stand in for two rounds of pitches, each round costing $2. What is your marginal cost of batting the second round? What is the average cost of batting two rounds?- Using the table below, answer the following questions.
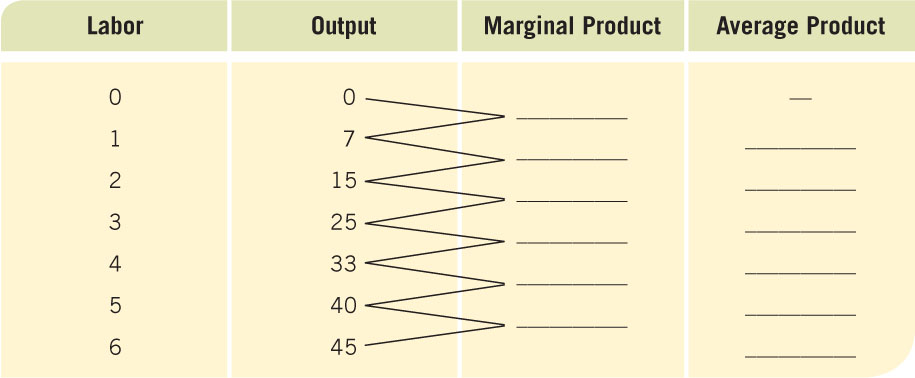
Question
Complete the table, filling in the answers for marginal and average products.
Prob 7 16a. Complete the table, filling in the answers for marginal and average products.Question
Over how many workers is the firm enjoying increasing returns?
Prob 7 16b. Over how many workers is the firm enjoying increasing returns?Question
At what number of workers do diminishing returns set in?
Prob 7 16c. At what number of workers do diminishing returns set in?Question
Are negative returns shown in the table?
Prob 7 16d. Are negative returns shown in the table?

Question
According to By the Numbers, explain why a correlation exists between the costs of industrial robots and the productivity rate over the last 20 years.
Prob 7 17. According to By the Numbers, explain why a correlation exists between the costs of industrial robots and the productivity rate over the last 20 years.Question
According to By the Numbers, between which four years from 2000 to 2012 did Internet flight bookings increase the most (by percentage of overall sales)? Between which four years from 2000 to 2012 did Internet flight check-ins increase the most (by percentage of overall check-ins)?
Prob 7 18. According to By the Numbers, between which four years from 2000 to 2012 did Internet flight bookings increase the most (by percentage of overall sales)? Between which four years from 2000 to 2012 did Internet flight check-ins increase the most (by percentage of overall check-ins)?