Elasticity
Multiple Choice Questions
After watching the Elasticity video lecture, consider the question(s) below. Then “submit” your response.
Question
1. When an airline company raises the price of tickets for a certain flight by 10%, it experiences an 8% decline in the number of passengers on that flight. The price elasticity of demand for the tickets on this particular flight is:
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
Question
2. The price elasticity of demand the figure is: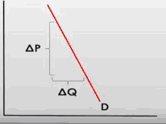
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
Question
3. A certain brand of breakfast cereal increases its price by 20%, while other brands keep their prices unchanged. The quantity of cereal sold by the brand that increases its price declines, and the quantity sold by the other brands increases. In this case, the cross price elasticity of demand between the cereal of the brand that increases its price and the cereals produced by other brands is:
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
Question
4. If the price elasticity of demand for a good is inelastic and the price of the good rises, the revenue of the firm selling the good will:
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
Question
5. The cross price elasticity of demand measures:
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
Question
6. If the cross price elasticity of demand is positive for a given pair of goods, they are _____ and if it is negative, they are _____
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
Question
7. A(n) _____ good is a good for which the amount consumed declines as a consumer’s income increases.
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
True/False Questions
After watching the Elasticity video lecture, consider the question(s) below. Then “submit” your response.
Question
1. Price elasticity of demand measures how responsive consumers are to changes in price.
| A. |
| B. |
Question
2. A normal good is one for which the quantity demanded increases as income increases.
| A. |
| B. |
Question
3. The price elasticity of supply measures the relationship between changes in quantity demanded of a good and changes in its quantity supplied.
| A. |
| B. |
Short Answer/Discussion Questions
After watching the Elasticity video lecture, consider the question(s) below. Then “submit” your response.
Question
1. One of the determinants of the price elasticity of demand is time. If gasoline prices increase substantially, what adjustments might consumers make over the long run that would increase their responsiveness to changes in the price of gasoline?
Question
2. How does knowledge of price elasticity of demand for a firm’s products help a firm make decisions regarding price increases?
Question
3. How is the concept of cross price elasticity of demand relevant for a business owner?