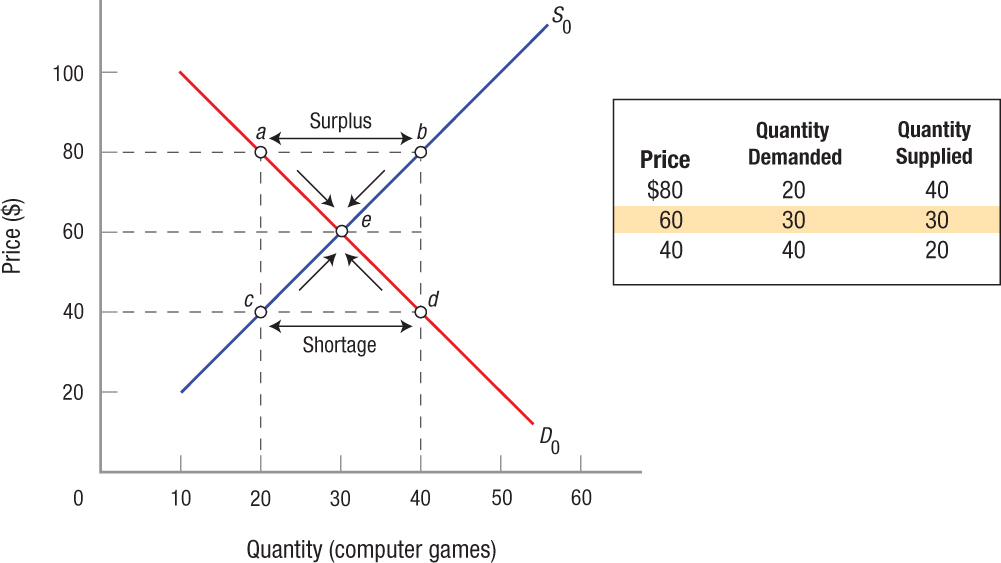
Equilibrium Price and Quantity of Computer Games Market equilibrium is achieved when quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. In this graph, that equilibrium occurs at point e, at an equilibrium price of $60 and an equilibrium output of 30. If the market price is above equilibrium ($80), a surplus of 20 computer games will result (b − a), and market forces would drive the price back down to $60. When the market price is too low ($40), a shortage of 20 computer games will result (d − c), and businesses will raise the offering prices until equilibrium is again restored.