Questions and Problems
Check Your Understanding
Question
The Phillips curve for the United States in the 1960s shown in Figure 4 becomes very steep after unemployment drops below 4%, and rather shallow as unemployment exceeds 6%. Why is a typical Phillips curve shaped this way?
Prob 14 1. The Phillips curve for the United States in the 1960s shown in Figure 4 becomes very steep after unemployment drops below 4%, and rather shallow as unemployment exceeds 6%. Why is a typical Phillips curve shaped this way?Question
Does the long-run Phillips curve make it difficult (if not impossible) for policymakers to increase output and employment beyond full employment in the long run?
Prob 14 2. Does the long-run Phillips curve make it difficult (if not impossible) for policymakers to increase output and employment beyond full employment in the long run?Question
Explain why inflation accelerates if policymakers use monetary and fiscal policy to keep unemployment below the natural rate.
Prob 14 3. Explain why inflation accelerates if policymakers use monetary and fiscal policy to keep unemployment below the natural rate.Question
Does having rational expectations mean that all economic actors act rationally and are always correct?
Prob 14 4. Does having rational expectations mean that all economic actors act rationally and are always correct?Question
Would policymakers prefer a Phillips curve with a steep or a shallow slope? Why?
Prob 14 5. Would policymakers prefer a Phillips curve with a steep or a shallow slope? Why?Question
A negative supply shock (a huge natural disaster or significant energy price spike) would do what to the short-run Phillips curve? To the long-run Phillips curve?
Prob 14 6. A negative supply shock (a huge natural disaster or significant energy price spike) would do what to the short-run Phillips curve? To the long-run Phillips curve?
Apply the Concepts
Question
Why would policymakers want to drive unemployment below the natural rate, given that inflation will result?
Prob 14 7. Why would policymakers want to drive unemployment below the natural rate, given that inflation will result?Question
Why are inflationary expectations so important for policymakers to keep under control? When a supply shock such as an oil price spike hits the economy, does it matter how fast policymakers attempt to bring the economy back to full employment?
Prob 14 8. Why are inflationary expectations so important for policymakers to keep under control? When a supply shock such as an oil price spike hits the economy, does it matter how fast policymakers attempt to bring the economy back to full employment?Question
How are the long-run Phillips curve (LRPC) and the long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) curve related?
Prob 14 9. How are the long-run Phillips curve (LRPC) and the long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) curve related?Question
Would the credibility of policymakers’ (Congress and the Fed) commitment to keeping inflation low have an effect on inflationary expectations when the economy is beset by a supply shock?
Prob 14 10. Would the credibility of policymakers’ (Congress and the Fed) commitment to keeping inflation low have an effect on inflationary expectations when the economy is beset by a supply shock?Question
Explain why those who favor the rational expectations approach to modeling the economy do not favor discretionary policymaking.
Prob 14 11. Explain why those who favor the rational expectations approach to modeling the economy do not favor discretionary policymaking.Question
If efficiency wages are widespread throughout the economy but most workers feel they are significantly underpaid, will paying workers more prevent them from shirking?
Prob 14 12. If efficiency wages are widespread throughout the economy but most workers feel they are significantly underpaid, will paying workers more prevent them from shirking?
In the News
Question
Fed Chairman Ben Bernanke noted that “in the 1970s the public had little confidence that the Fed would keep inflation low and stable.” As a result, when oil prices rose, wages and prices quickly followed. This caused the Fed to have to increase interest rates sharply to curtail inflation. Do people have a different perspective on the Fed today than they did in the past?
Prob 14 13. Fed Chairman Ben Bernanke noted that “in the 1970s the public had little confidence that the Fed would keep inflation low and stable.” As a result, when oil prices rose, wages and prices quickly followed. This caused the Fed to have to increase interest rates sharply to curtail inflation. Do people have a different perspective on the Fed today than they did in the past?Question
About every year, Congress is tasked with increasing the debt ceiling that allows the government to continue borrowing. In past decades, such legislation would pass easily because it was authorizing the payment of expenses already incurred. However, in recent years, congressional leaders took the drastic approach to oppose raising the debt ceiling as a way to reign in government spending. If these leaders were successful in preventing the debt ceiling from being raised, what would be some benefits and costs of this action?
Prob 14 14. About every year, Congress is tasked with increasing the debt ceiling that allows the government to continue borrowing. In past decades, such legislation would pass easily because it was authorizing the payment of expenses already incurred. However, in recent years, congressional leaders took the drastic approach to oppose raising the debt ceiling as a way to reign in government spending. If these leaders were successful in preventing the debt ceiling from being raised, what would be some benefits and costs of this action?
Solving Problems
Question
In Canada, the consensus estimate of the natural rate of unemployment was 4.5% in 1970 and 7% in 2005. A minority view has claimed that the change to 7% is beyond explanation and must be too high. A similar change has taken place in the United States over this period, but the consensus estimate of the natural rate of unemployment is closer to 5.5% today. What would be the result if the Bank of Canada (the central bank of Canada) and the Federal Reserve in the United States assumed that the natural rate was 7% when it really was closer to 5.5%?
Prob 14 15. In Canada, the consensus estimate of the natural rate of unemployment was 4.5% in 1970 and 7% in 2005. A minority view has claimed that the change to 7% is beyond explanation and must be too high. A similar change has taken place in the United States over this period, but the consensus estimate of the natural rate of unemployment is closer to 5.5% today. What would be the result if the Bank of Canada (the central bank of Canada) and the Federal Reserve in the United States assumed that the natural rate was 7% when it really was closer to 5.5%?Question
When the recessions of 1990–1991 and 2001 ended, unemployment kept rising and it took roughly two-and-a-half years before unemployment returned to where it was at the trough of the recession. The figure below shows the path of unemployment (indexed to 100 = trough level) after the recession had officially ended.
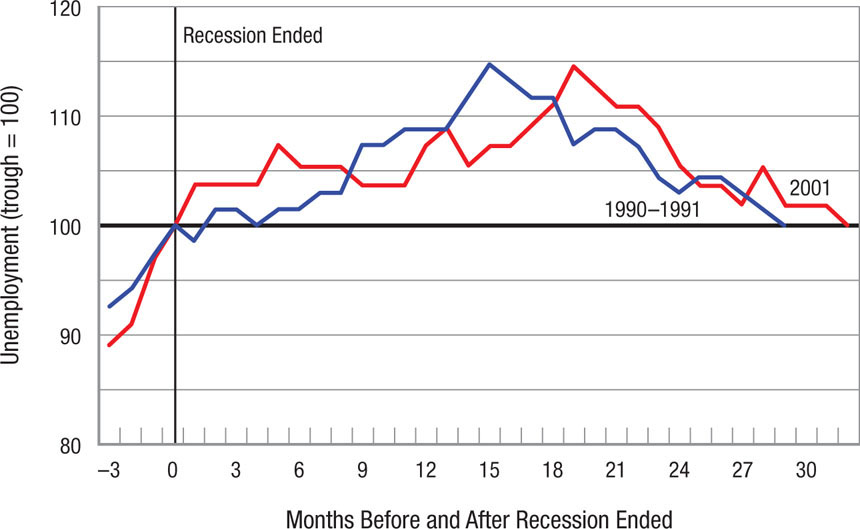
Following the 1990–1991 recession, unemployment only returned to its lowest level (at the peak before the recession) after four-and-a-half years, and with the recession of 2001, unemployment never returned to its lowest level. Does this phenomenon of unemployment continuing to rise after a recession has ended help foster the conclusion that these two recoveries were jobless recoveries?Prob 14 16. When the recessions of 1990–1991 and 2001 ended, unemployment kept rising and it took roughly two-and-a-half years before unemployment returned to where it was at the trough of the recession. The figure below shows the path of unemployment (indexed to 100 = trough level) after the recession had officially ended.Following the 1990–1991 recession, unemployment only returned to its lowest level (at the peak before the recession) after four-and-a-half years, and with the recession of 2001, unemployment never returned to its lowest level. Does this phenomenon of unemployment continuing to rise after a recession has ended help foster the conclusion that these two recoveries were jobless recoveries?

Question
According to By the Numbers, in which year did the median value of existing homes peak? By what percentage did the median existing home price increase from the year 2000 until its peak? By what percentage did the median existing home price fall from its peak to the year 2012?
Prob 14 17. According to By the Numbers, in which year did the median value of existing homes peak? By what percentage did the median existing home price increase from the year 2000 until its peak? By what percentage did the median existing home price fall from its peak to the year 2012?Question
According to By the Numbers, what was the value of monthly real retail sales when it reached its lowest point in 2009? By what percentage did monthly real retail sales increase from 2009 to 2013?
Prob 14 18. According to By the Numbers, what was the value of monthly real retail sales when it reached its lowest point in 2009? By what percentage did monthly real retail sales increase from 2009 to 2013?