Questions and Problems
Check Your Understanding
Question
Describe the three measures of inflation in use today and the focus of each measure.
Prob 6 1. Describe the three measures of inflation in use today and the focus of each measure.Question
Who loses from unanticipated inflation? Who benefits?
Prob 6 2. Who loses from unanticipated inflation? Who benefits?Question
Describe the possible losses to our society and the economy when people are unemployed.
Prob 6 3. Describe the possible losses to our society and the economy when people are unemployed.Question
Why do teenagers and young people have high unemployment rates?
Prob 6 4. Why do teenagers and young people have high unemployment rates?Question
Describe the three types of unemployment. What types of government programs would be most effective in combating each type of unemployment?
Prob 6 5. Describe the three types of unemployment. What types of government programs would be most effective in combating each type of unemployment?Question
What is required for a person to be considered unemployed? How is the unemployment rate computed?
Prob 6 6. What is required for a person to be considered unemployed? How is the unemployment rate computed?
Apply the Concepts
Question
You have several student loans that have interest rates that change every year. After graduation, you can consolidate these loans into a fixed rate single loan. You can consolidate now or one year from now. How do your expectations of the inflation rate during the next year affect your decision regarding when to consolidate?
Prob 6 7. You have several student loans that have interest rates that change every year. After graduation, you can consolidate these loans into a fixed rate single loan. You can consolidate now or one year from now. How do your expectations of the inflation rate during the next year affect your decision regarding when to consolidate?Question
Suppose you work hard at a job after graduation and after your first year, your effort is rewarded with a 3% raise when the average wage increase in your company is 2%. Then, the government releases its inflation report that states that inflation is running at 5%. Given this information, did your standard of living improve? Why or why not?
Prob 6 8. Suppose you work hard at a job after graduation and after your first year, your effort is rewarded with a 3% raise when the average wage increase in your company is 2%. Then, the government releases its inflation report that states that inflation is running at 5%. Given this information, did your standard of living improve? Why or why not?Question
Since 1980, the U.S. population has grown 38%, while employment has increased by 45%. Further, the number of people unemployed has risen by only 15%. Are all of these indicators a sign of a strong or a weak labor market?
Prob 6 9.Since 1980, the U.S. population has grown 38%, while employment has increased by 45%. Further, the number of people unemployed has risen by only 15%. Are all of these indicators a sign of a strong or a weak labor market?Question
Assume you just lost your job and have decided to take a month-long break to travel to Europe before looking for a new position. Just as you return home from your trip, you are interviewed by the Department of Labor about your employment status. How would you be classified (employed, unemployed, or not in the labor force)?
Prob 6 10.Assume you just lost your job and have decided to take a month-long break to travel to Europe before looking for a new position. Just as you return home from your trip, you are interviewed by the Department of Labor about your employment status. How would you be classified (employed, unemployed, or not in the labor force)?Question
The Bureau of Labor Statistics categorizes unemployed people into several groups, including job leavers, job losers, and discouraged workers. During a mild recession, which group would tend to increase the most? During a deep recession? During a boom?
Prob 6 11.The Bureau of Labor Statistics categorizes unemployed people into several groups, including job leavers, job losers, and discouraged workers. During a mild recession, which group would tend to increase the most? During a deep recession? During a boom?Question
In the beginning of a recovery after a recession, employment begins to rise and the news media report these data on job growth. Would such a report have an impact on the labor force? Would it affect the unemployment rate?
Prob 6 1.In the beginning of a recovery after a recession, employment begins to rise and the news media report these data on job growth. Would such a report have an impact on the labor force? Would it affect the unemployment rate?
In the News
Question
In early 2013, when the United States came close to experiencing a “fiscal cliff,” one politician proposed introducing a trillion dollar coin to be minted by the government and sent to the U.S. Treasury to pay down the federal deficit (“Economics Is Platinum: What the Trillion-Dollar Coin Teaches Us,” Bloomberg.com, January 14, 2013). If such a coin were to be minted, what would be the likely effects on inflation? Is this a risk-free way of paying off a fiscal deficit? Why or why not?
Prob 6 13. In early 2013, when the United States came close to experiencing a “fiscal cliff,” one politician proposed introducing a trillion dollar coin to be minted by the government and sent to the U.S. Treasury to pay down the federal deficit (“Economics Is Platinum: What the Trillion-Dollar Coin Teaches Us,” Bloomberg.com, January 14, 2013). If such a coin were to be minted, what would be the likely effects on inflation? Is this a risk-free way of paying off a fiscal deficit? Why or why not?Question
Federal unemployment benefits were extended in 2013, allowing unemployed workers to receive up to 73 weeks of benefits depending on the unemployment rate in each state. This is an extension of a program that at its peak during the last recession offered up to a maximum of 99 weeks of unemployment benefits. How does extending the federal unemployment benefit program influence the unemployment rate?
Prob 6 14. Federal unemployment benefits were extended in 2013, allowing unemployed workers to receive up to 73 weeks of benefits depending on the unemployment rate in each state. This is an extension of a program that at its peak during the last recession offered up to a maximum of 99 weeks of unemployment benefits. How does extending the federal unemployment benefit program influence the unemployment rate?
Solving Problems
Question
In January 1980, the CPI stood at 77.8, and by January 2006, it was 198.3. By what percent have consumer prices increased over this period? Assume college graduates entering the job market were being paid on average $1,200 a month in 1980, and in January 2006 the average was $3,000. Were these newer graduates paid more or less after adjusting for inflation?
Prob 6 15. In January 1980, the CPI stood at 77.8, and by January 2006, it was 198.3. By what percent have consumer prices increased over this period? Assume college graduates entering the job market were being paid on average $1,200 a month in 1980, and in January 2006 the average was $3,000. Were these newer graduates paid more or less after adjusting for inflation?- Given the data for the United States between 1960 and 2010, complete the table below and answer the questions that follow.
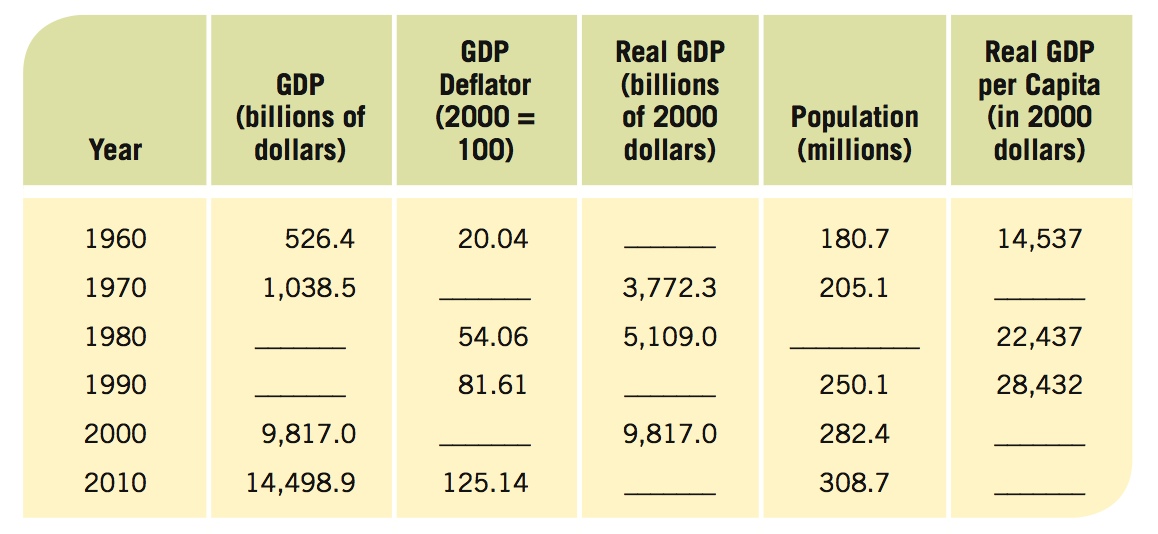
Question
Between 1960 and 2010:
i. GDP was how many times larger in 2010 than in 1960?
ii. The price level was how many times larger in 2010 than in 1960?
iii. Real GDP was how many times larger in 2010 than in 1960?
iv. What is the relationship between these values?Prob 6 16a.Between 1960 and 2010:GDP was how many times larger in 2010 than in 1960?The price level was how many times larger in 2010 than in 1960?Real GDP was how many times larger in 2010 than in 1960?What is the relationship between these values?Question
What was the percentage change in real GDP per capita between 1960 and 2010? Were people in the United States better off in 2010 than in 1960?
Prob 6 16b. What was the percentage change in real GDP per capita between 1960 and 2010? Were people in the United States better off in 2010 than in 1960?Question
What are some of the problems associated with using real GDP per capita as a measure of our well-being?
Prob 6 16c. What are some of the problems associated with using real GDP per capita as a measure of our well-being?

Question
According to By the Numbers, which of the previous four presidents (R. Reagan, G. H. W. Bush, B. Clinton, G. W. Bush) saw a fall in the Misery Index from the year he entered office to the year he left? Which presidents saw a rise in the Misery Index?
Prob 6 17. According to By the Numbers, which of the previous four presidents (R. Reagan, G. H. W. Bush, B. Clinton, G. W. Bush) saw a fall in the Misery Index from the year he entered office to the year he left? Which presidents saw a rise in the Misery Index?Question
Using By the Numbers, compare the increase in the average prices of tuition at public and private colleges and universities with the increase in overall prices according to the consumer price index from 2001 to 2012.
Prob 6 18. Using By the Numbers, compare the increase in the average prices of tuition at public and private colleges and universities with the increase in overall prices according to the consumer price index from 2001 to 2012.