Chapter Introduction
309

310
After studying this chapter you should be able to:
- Describe the impact of the supply of land on markets.
- Determine the present value of an investment.
- Compute the rate of return of an investment.
- Describe how businesses acquire financial capital.
- Understand how debt and equity instruments work and the differences between them.
- Describe the relationship between education and earnings.
- Know how market equilibrium levels for human capital are determined.
- Describe the different forms of on-the-job training and why both employers and employees benefit from it.
- Describe the impact of economic profits on entrepreneurs and markets.
- Explain the role of innovation in improving standards of living.
Have you ever dreamed of venturing into space without having to undergo years of astronaut training? Richard Branson, the CEO of Virgin Group, wants to make that dream a reality with the launch of Virgin Galactic airlines. Already an innovator in the aerospace industry, Branson’s new space travel service will take six passengers at a time on a 3.5-hour suborbital flight 65 miles above the Earth’s surface, allowing passengers to experience several minutes of weightlessness before the spacecraft returns to Earth. How does a business like Virgin Galactic go about creating its service and what resources would it need?
In the previous chapter, we studied how businesses rely on labor markets to acquire the workers needed to produce their products. To build a technologically advanced product such as a space plane, much more than labor is needed. First, the firm must buy abundant amounts of capital inputs, such as aluminum, glass, and engines, in addition to the massive machinery required to put the plane together. Second, the firm must obtain the financial resources to fund the operation until the planes are built, placed into service, and generate revenue. Third, the firm must find labor that has the knowledge to build airplanes. For Virgin Galactic, it would seek workers who studied aerospace engineering in college or those who have acquired skills from previous jobs, such as serving in the Air Force. Last, the firm must have the overall vision to provide the market with what it wants—or what it thinks the market will want in the immediate future.
Although space travel might be just a dream for those unable to afford the expensive ride, examples of innovation abound in the aerospace industry. If you have recently flown on a commercial airliner, you may have noticed the technological innovations that are becoming more prevalent on airplanes. In some aircraft, you can now watch live TV, view movies on demand, and even browse the Internet. Such features are just some of the amenities airlines are offering to make airline travel more enjoyable. Further, innovations in aircraft operation, such as lighter composite materials used in new aircraft, will allow significant savings in fuel, the largest cost component of airlines. Developing a plane that provides customers with new amenities while cutting operating costs is a major goal of the aerospace industry.
The necessary inputs (also called factors) for the production of commercial spaceships and airplanes require firms to use other resource markets, such as those for land and capital, in addition to the labor market. Land markets are used to obtain actual land along with natural resources. Capital markets are used to obtain physical capital, financial capital, and human capital.
311
Innovation Is the Cornerstone of Growth
Innovation is the use of ideas and knowledge to produce new goods and services that raise a country’s standard of living. Human capital and financial capital are important drivers of innovation that lead to economic growth.
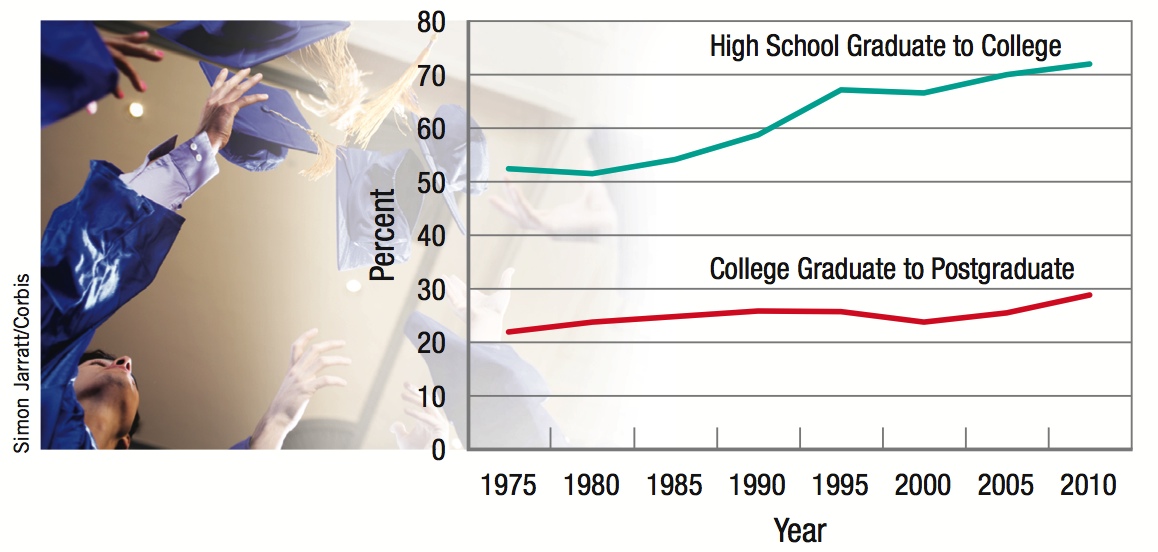
Human capital investment has grown over the past 35 years as the percent of high school graduates enrolling in college continues to increase. The percent of college graduates pursuing postgraduate degrees also has steadily increased.
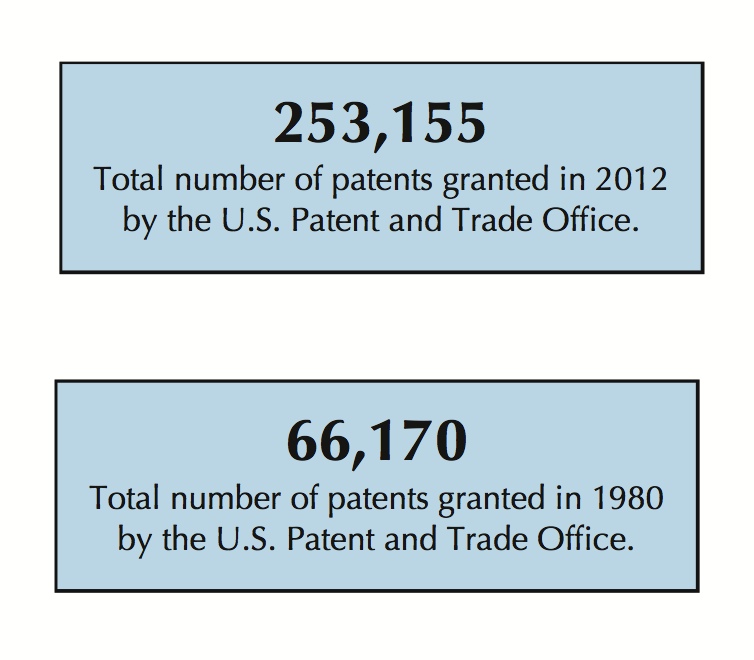
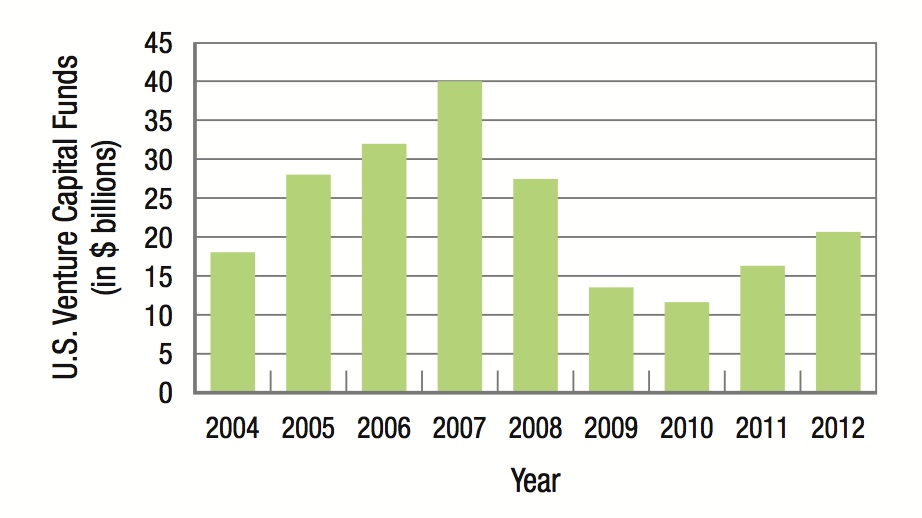
Venture capital firms provide financial capital to entrepreneurs to produce new products that lead to economic growth. The 2007–2009 recession dramatically reduced the amount of venture capital funds available.
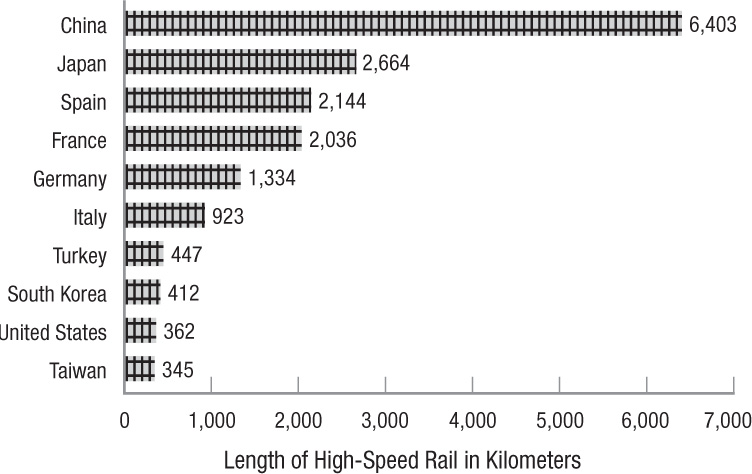
The development of high-speed rail travel (defined as rail travel over 150 mph) is an innovation that saves time and costs in transporting passengers and freight. As of January 2013, China led the world in total length of high-speed rail in kilometers currently in operation as well as the amount of planned new railways over the next decade.
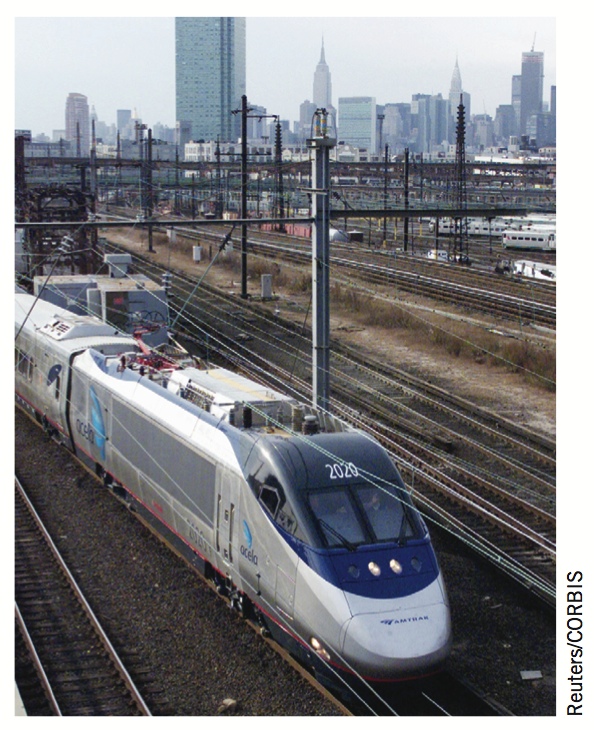

The Acela from Washington, D.C., to Boston is the only high-speed rail service currently in operation in the United States, with a top speed of 150 mph.
312
This chapter begins with an analysis of the land market, followed by a study of the three capital markets and the role that each plays in the economy. The chapter concludes with a discussion of entrepreneurship, the factor of production that brings all physical inputs together to generate profits and leads to innovation that increases economic growth.