Questions and Problems
Check Your Understanding
Question
Why must price cover average variable costs if the firm is to continue operating?
Prob 8 1. Why must price cover average variable costs if the firm is to continue operating?Question
Why do perfectly competitive firms sell their products only at the market price? Why not try to raise prices to make more profit or lower them to garner more sales?
Prob 8 2. Why do perfectly competitive firms sell their products only at the market price? Why not try to raise prices to make more profit or lower them to garner more sales?Question
Describe the role that easy entry and exit play in competitive markets over the long run.
Prob 8 3. Describe the role that easy entry and exit play in competitive markets over the long run.Question
Why are marginal revenue and price equal for the perfectly competitive firm?
Prob 8 4. Why are marginal revenue and price equal for the perfectly competitive firm?Question
Why, if competitive firms are earning economic profits in the short run, are they unable to earn them in the long run?
Prob 8 5. Why, if competitive firms are earning economic profits in the short run, are they unable to earn them in the long run?Question
Describe the reasons why an industry’s costs might increase in the long run. Why might they decrease over the long run?
Prob 8 6. Describe the reasons why an industry’s costs might increase in the long run. Why might they decrease over the long run?
Apply the Concepts
Question
When a sports team consistently struggles, one strategy is to replace the coach. But when this happens, the new coach initially has the same players (its primary input). How can a new coach improve the team’s record when the players are mostly the same?
Prob 8 7. When a sports team consistently struggles, one strategy is to replace the coach. But when this happens, the new coach initially has the same players (its primary input). How can a new coach improve the team’s record when the players are mostly the same?Question
How is the short-run supply curve for the competitive firm determined?
Prob 8 8. How is the short-run supply curve for the competitive firm determined?Question
Suppose you master the art of growing herbs in your garden and selling them for profit at the local farmer’s market. Your neighbor sees your profitable business and decides to do the same, however with less experience he faces a much higher marginal cost curve. How is it possible for both you and your neighbor to sell herbs at the same price?
Prob 8 9. Suppose you master the art of growing herbs in your garden and selling them for profit at the local farmer’s market. Your neighbor sees your profitable business and decides to do the same, however with less experience he faces a much higher marginal cost curve. How is it possible for both you and your neighbor to sell herbs at the same price?Question
Assume a competitive industry is in long-run equilibrium and firms in the industry are earning normal profits. Now assume that production technology improves such that average total cost declines by $5 per unit. Describe the process this industry will go through as it moves to a new long-run equilibrium.
Prob 8 10. Assume a competitive industry is in long-run equilibrium and firms in the industry are earning normal profits. Now assume that production technology improves such that average total cost declines by $5 per unit. Describe the process this industry will go through as it moves to a new long-run equilibrium.Question
When a competitive firm is earning economic profits, is it also maximizing profit per unit? Why or why not?
Prob 8 11. When a competitive firm is earning economic profits, is it also maximizing profit per unit? Why or why not?Question
In this chapter we suggested that whenever market price fell below average variable costs, the firm would shut down. At that point revenue is not covering its variable costs and the firm is losing more money than if it just shut down and lost fixed costs. Clearly, shutting the firm is more complicated than that. Under what circumstances might the firm continue to operate even though prices are below average variable costs?
Prob 8 12. In this chapter we suggested that whenever market price fell below average variable costs, the firm would shut down. At that point revenue is not covering its variable costs and the firm is losing more money than if it just shut down and lost fixed costs. Clearly, shutting the firm is more complicated than that. Under what circumstances might the firm continue to operate even though prices are below average variable costs?
In the News
Question
A January 25, 2012, article in The New York Times describes how more states are attempting to pass legislation to collect sales tax on Internet sales (sometimes dubbed the Amazon Tax) even when the seller does not have a physical presence in that state. Given the intense competition between online retailers and physical (brick-and-mortar) stores, how would such laws affect competition? Would brick-and-mortar stores be better off ? How about customers? Why or why not?
Prob 8 13. A January 25, 2012, article in The New York Times describes how more states are attempting to pass legislation to collect sales tax on Internet sales (sometimes dubbed the Amazon Tax) even when the seller does not have a physical presence in that state. Given the intense competition between online retailers and physical (brick-and-mortar) stores, how would such laws affect competition? Would brick-and-mortar stores be better off ? How about customers? Why or why not?Question
An April 19, 2012, article by Art Carden in Forbes entitled “Let’s Be Blunt: It’s Time to End the Drug War” argues that legalizing marijuana is a key solution to ending the drug war. He argues that turning the industry into a competitive market would force cost-inefficient drug cartels to exit the market. Using what you know about competitive markets and firm entry and exit, explain the economics behind the author’s theory.
Prob 8 14. An April 19, 2012, article by Art Carden in Forbes entitled “Let’s Be Blunt: It’s Time to End the Drug War” argues that legalizing marijuana is a key solution to ending the drug war. He argues that turning the industry into a competitive market would force cost-inefficient drug cartels to exit the market. Using what you know about competitive markets and firm entry and exit, explain the economics behind the author’s theory.
Solving Problems
- Use the following figure for a firm in a perfectly competitive market.
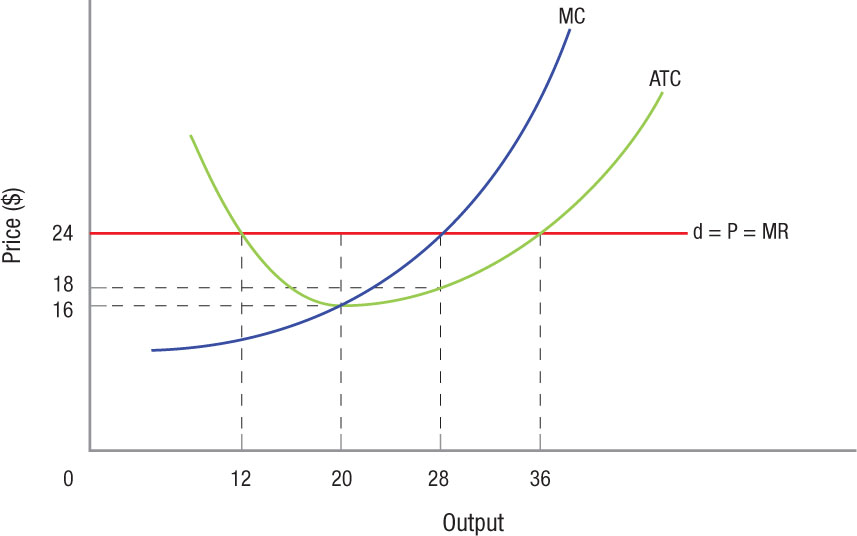
Question
What is the output that maximizes the firm’s profit?
Prob 8 15a. What is the output that maximizes the firm’s profit?Question
At the profit-maximizing output, calculate total revenue and total cost.
Prob 8 15b. At the profit-maximizing output, calculate total revenue and total cost.Question
If the firm maximizes profit, how much profit does it earn?
Prob 8 15c. If the firm maximizes profit, how much profit does it earn?Question
What will likely happen to market demand or market supply in the long run?
Prob 8 15d. What will likely happen to market demand or market supply in the long run?Question
What will likely happen to the market price in the long run?
Prob 8 15e. What will likely happen to the market price in the long run?
- Use the figure below to answer the following true/false questions:
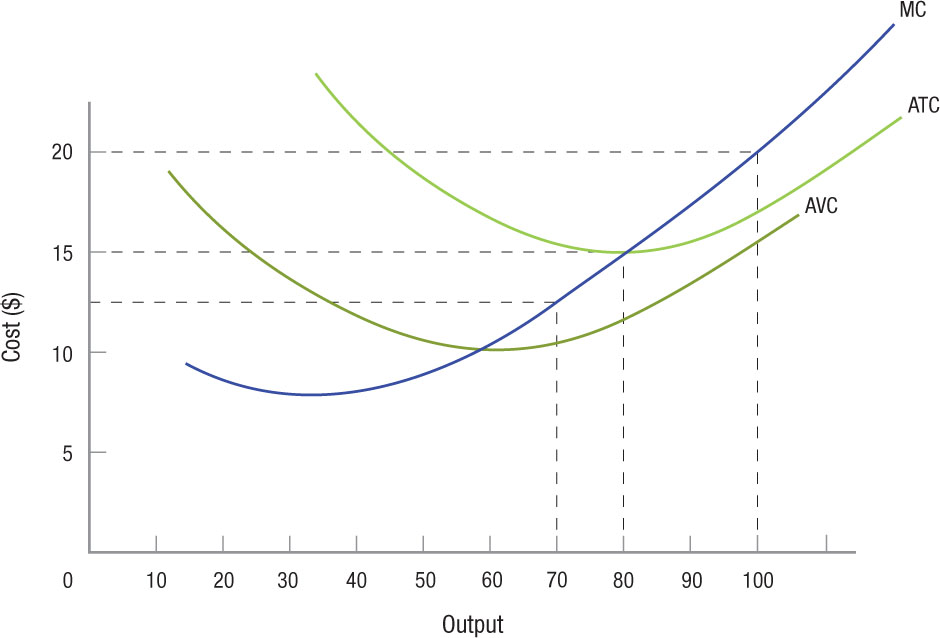
Question
If market price is $25, the firm earns economic profits.
Prob 8 16a. If market price is $25, the firm earns economic profits.Question
If market price is $20, the firm earns economic profit equal to roughly $100.
Prob 8 16b. If market price is $20, the firm earns economic profit equal to roughly $100.Question
If market price is $9, the firm produces roughly 55 units.
Prob 8 16c. If market price is $9, the firm produces roughly 55 units.Question
If market price is $12.50, the firm produces roughly 70 units and makes an economic loss equal to roughly $210.
Prob 8 16d. If market price is $12.50, the firm produces roughly 70 units and makes an economic loss equal to roughly $210.Question
Total fixed costs for this firm are roughly $100.
Prob 8 16e. Total fixed costs for this firm are roughly $100.Question
If market price is $15, the firm sells 80 units and makes a normal profit.
Prob 8 16f. If market price is $15, the firm sells 80 units and makes a normal profit.

Question
According to By the Numbers, which two regions employ the highest number of people in the farm and farm-related industries? Approximately how many total persons are employed in the farm and farm-related industries in these two regions combined?
Prob 8 17. According to By the Numbers, which two regions employ the highest number of people in the farm and farm-related industries? Approximately how many total persons are employed in the farm and farm-related industries in these two regions combined?Question
According to By the Numbers, in which year (since 1986) did the following crops reach their highest and lowest prices per bushel: corn, wheat, soybeans?
Prob 8 18. According to By the Numbers, in which year (since 1986) did the following crops reach their highest and lowest prices per bushel: corn, wheat, soybeans?