Game Theory
Multiple Choice Questions
After watching the Game Theory video lecture, consider the question(s) below. Then “submit” your response.
Question
1. Game theory is the study of how:
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
Question
2. A Nash equilibrium describes an outcome in which:
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
Question
3. When players in a game select a dominant strategy, they are:
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
Question
4. The payoff boxes show the strategic options and corresponding profits for two stores with respect to advertising spending (heavy or light). Based on this information, Target’s dominant advertising strategy is to: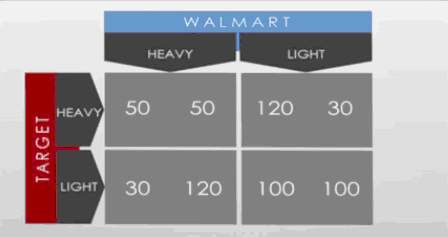
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
Question
5. In many instances, competitive companies could agree with each other on key strategic items, and produce higher profits than what competition allows. Reasons this is not done include the _____, and the illegality of collusion.
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
Question
6. While prisoner’s dilemma outcomes may produce worse results for competing companies than other alternate outcomes, such dilemmas can benefit:
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
Question
7. Some prisoner’s dilemma outcomes can be resolved when the players engage in:
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
True/False Questions
After watching the Game Theory video lecture, consider the question(s) below. Then “submit” your response.
Question
1. Game theory can be applied in business, political science, military planning, and sports.
| A. |
| B. |
Question
2. A Nash equilibrium always yields the best outcome for all participants in a game.
| A. |
| B. |
Question
3. Prisoner’s dilemma outcomes are uncommon.
| A. |
| B. |
Short Answer/Discussion Questions
After watching the Game Theory video lecture, consider the question(s) below. Then “submit” your response.
Question
1. Provide an example of a third party benefiting from a prisoner’s dilemma outcome while the game participants are worse off relative to other possible outcomes. Also, explain the nature of the benefit.
Question
2. How can a repeated game help in resolving a prisoner’s dilemma outcome?
Question
3. Why is game theory important to economics?