Externalities and Public Goods
Multiple Choice Questions
After watching the Externalities and Public Goods video lecture, consider the question(s) below. Then “submit” your response.
Question
1. An action taken by a person or business that affects the well-being of another individual or firm not involved in the transaction is called a(n):
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
Question
2. The inability of a market to generate a socially optimal quantity or price of a good is called a(n):
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
Question
3. Many companies choose to emit pollution instead of using cleaner production methods because of:
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
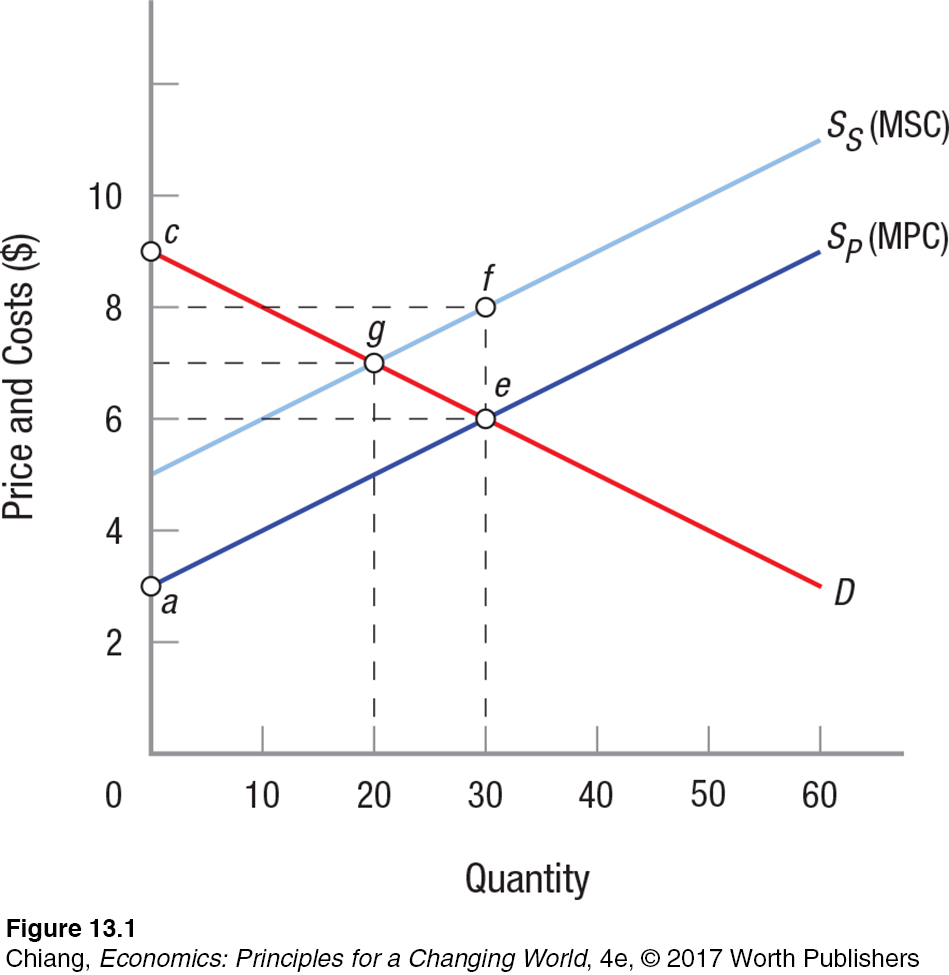
Question
4. Refer to Figure 13.1. The upper curve (SS) in the figure represents the _____ supply curve.
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
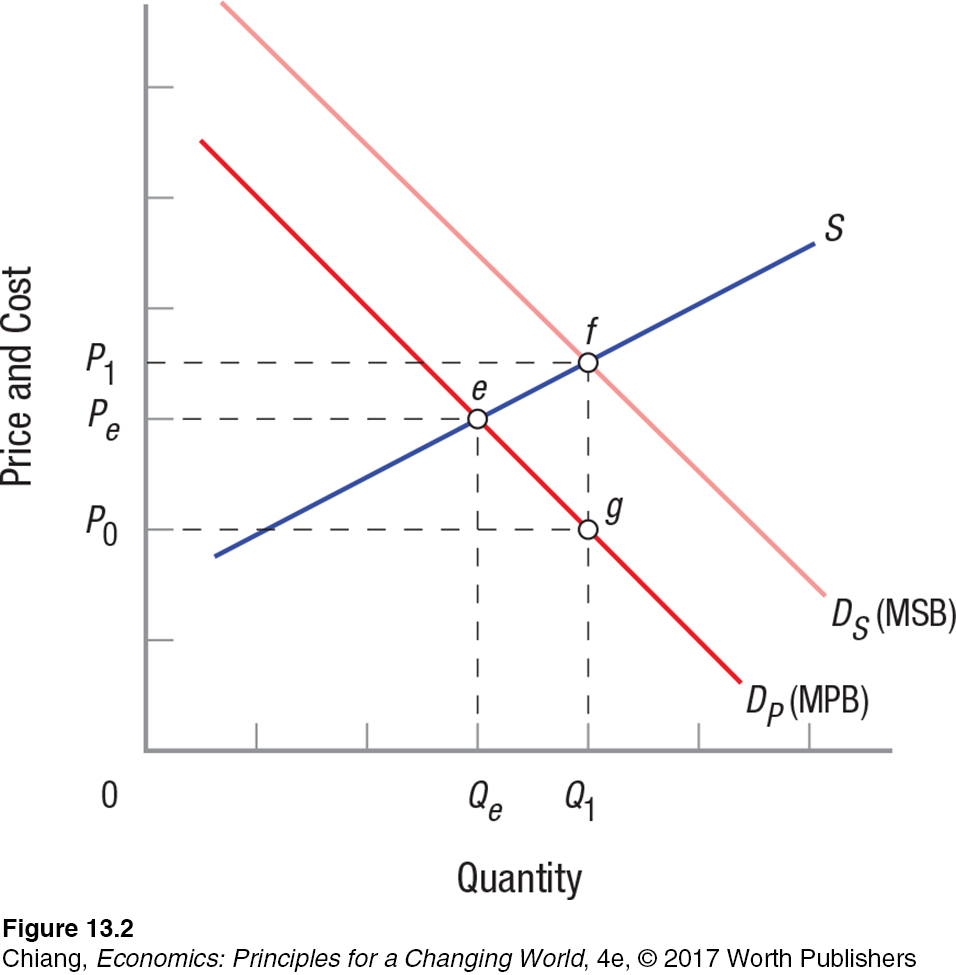
Question
5. Refer to Figure 13.2. The upper curve (DS) in the figure represents the _____ demand curve.
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
Question
6. Products that generate external costs are generally _____ or _____.
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
Question
7. Public goods are _____ and _____.
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
Question
8. A nonrival good is one for which:
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
Question
9. “Nonexcludable” means that:
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
Question
10. Common property resources tend to be exploited quickly because:
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
True/False Questions
After watching the Externalities and Public Goods video lecture, consider the question(s) below. Then “submit” your response.
Question
1. Goods generating positive externalities are over-produced or over-consumed.
| A. |
| B. |
Question
2. Keeping one’s front yard neat and attractive can create a positive externality.
| A. |
| B. |
Question
3. Public goods are both rival and excludable.
| A. |
| B. |
Short Answer/Discussion Questions
After watching the Externalities and Public Goods video lecture, consider the question(s) below. Then “submit” your response.
Question
1. Why might a business choose to emit pollution?
Question
2. Is a public beach both nonrival and nonexcludable? Explain.
Question
3. Why are public goods usually provided by the government?