Printed Page 669
The Long Road Back: The Great Recession and the Jobless Recovery
The Great Recession was caused by the collapse of the housing market, which led to reduced consumer sentiment and lower retail sales. Persistent unemployment ensued and the Fed used unprecedented monetary policy actions to speed up the economic recovery.
alexs/Getty Images
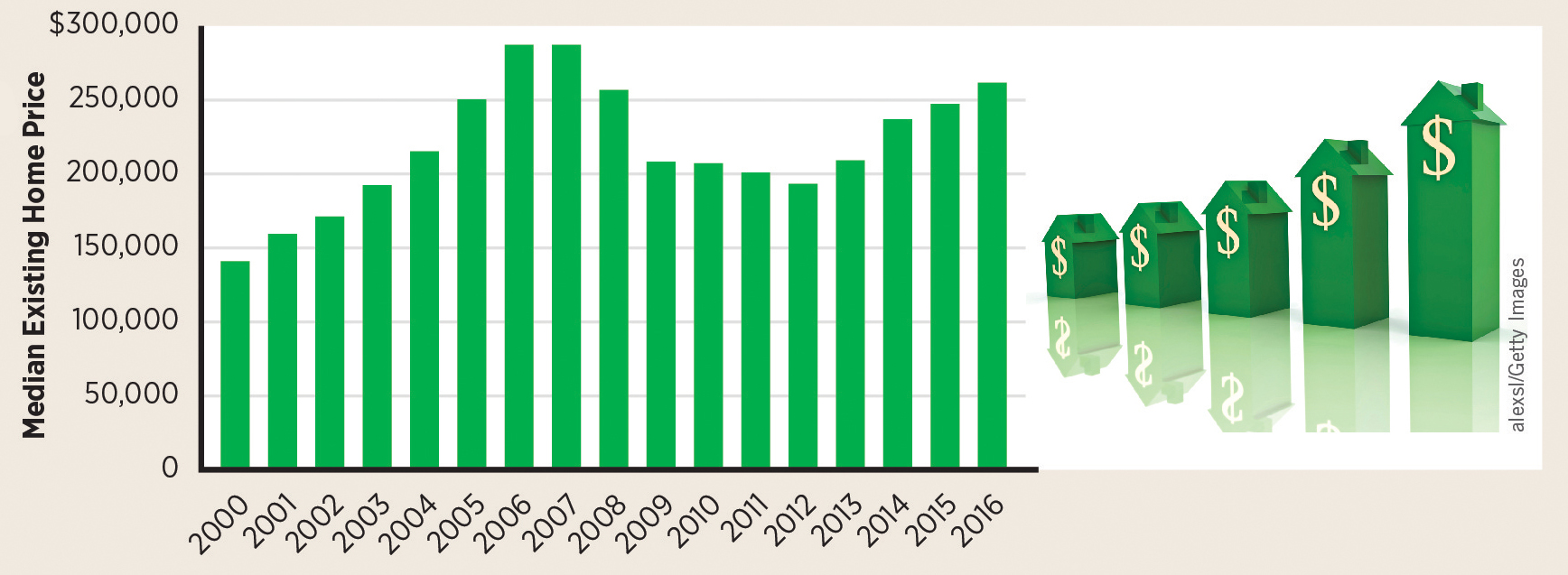
Median existing home prices rose significantly in the early years of the 21st century but fell quickly in the latter part of the decade. Housing prices have since risen again.
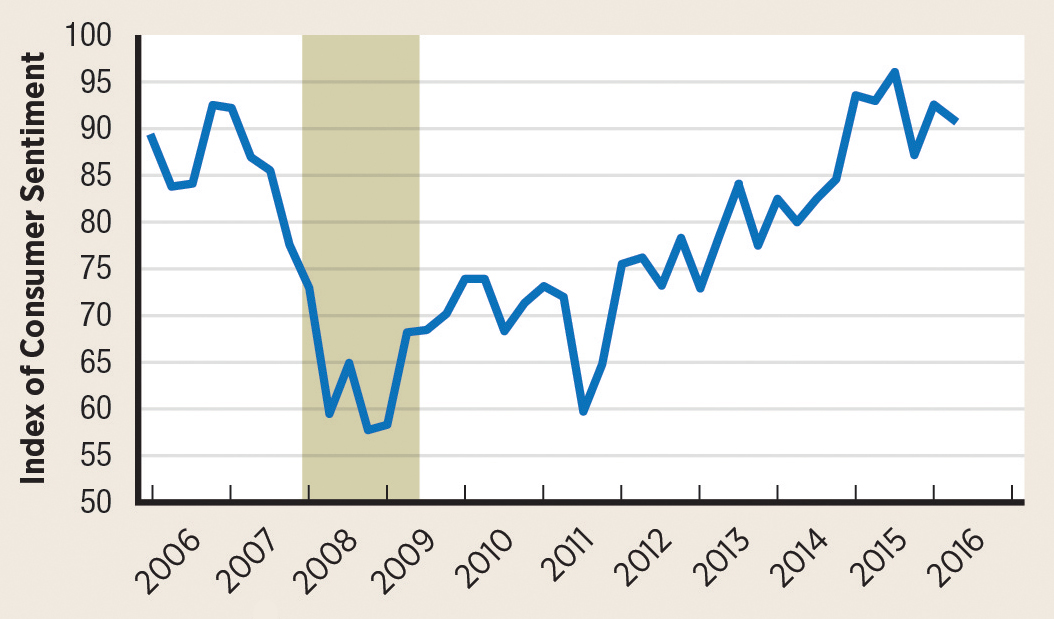
Consumer sentiment fell significantly from 2007 to 2009. It took six years of economic recovery before consumer sentiment returned to its pre-recession peak.
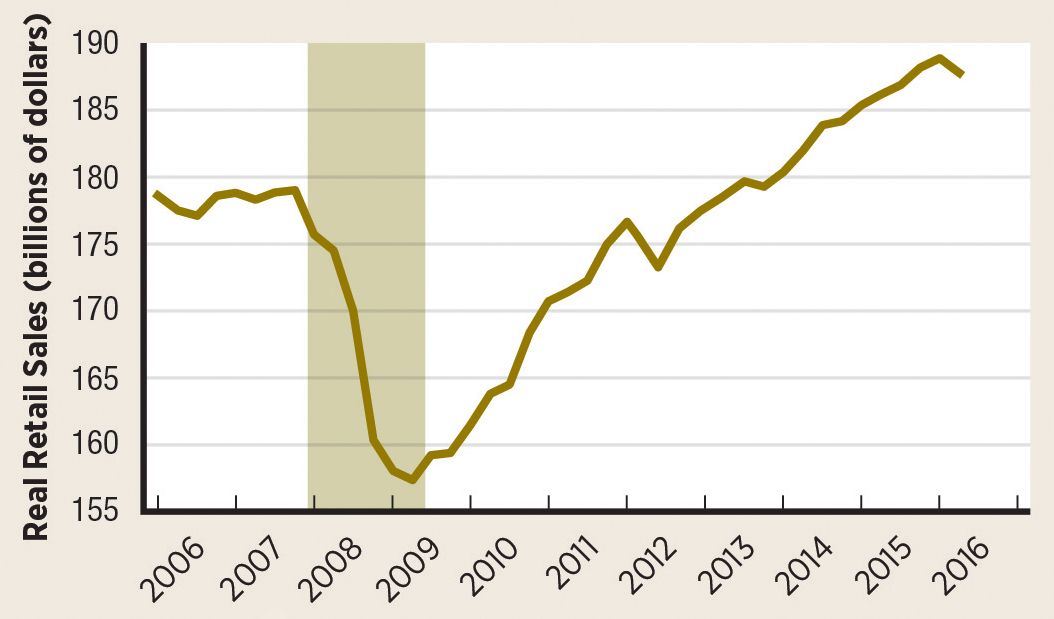
Monthly real retail sales fell over 10% from 2007 to 2009. It took four years for real retail sales to recover and to surpass the level reached in 2007.


Tupungato/Shutterstock
The Fed’s actions kept long-term interest rates low, encouraging consumers and businesses to borrow in order to consume and invest. Yet, banks increased their lending standards significantly after the last financial crisis, reducing the effect of low interest rates.
[Leave] [Close]