chapter summary
chapter summary
Section 1 Why Is Economic Growth Important?
7.1 Economic growth is the most important factor influencing a country’s standard of living. Economic growth is measured by a nation’s ability to increase real GDP and real GDP per capita. Using real values instead of nominal values allows a country to compare growth from year to year without having to take into account the effects of inflation. Countries with high economic growth have seen rising incomes and better lives for their citizens.
7.2 The Rule of 70 is a simple tool used to estimate the number of years it takes for a value to double given a constant growth rate.
Number of Years = 70/Growth Rate
Examples: Number of years to double at growth rate of
1%: 70/1 = 70 years
2%: 70/2 = 35 years
5%: 70/5 = 14 years
10%: 70/10 = 7 years
20%: 70/20 = 3.5 years

7.3 Using the Rule of 70 to estimate 5% versus 10% growth:
| Year | Value at 5% | Year | Value at 10% |
| 2017 | $1,000 | 2017 | $1,000 |
| 2024 | $2,000 | ||
| 2031 | $2,000 | 2031 | $4,000 |
| 2038 | $8,000 | ||
| 2045 | $4,000 | 2045 | $16,000 |
In 28 years, the initial $1,000 is worth $16,000 at 10% growth versus $4,000 at 5% growth.
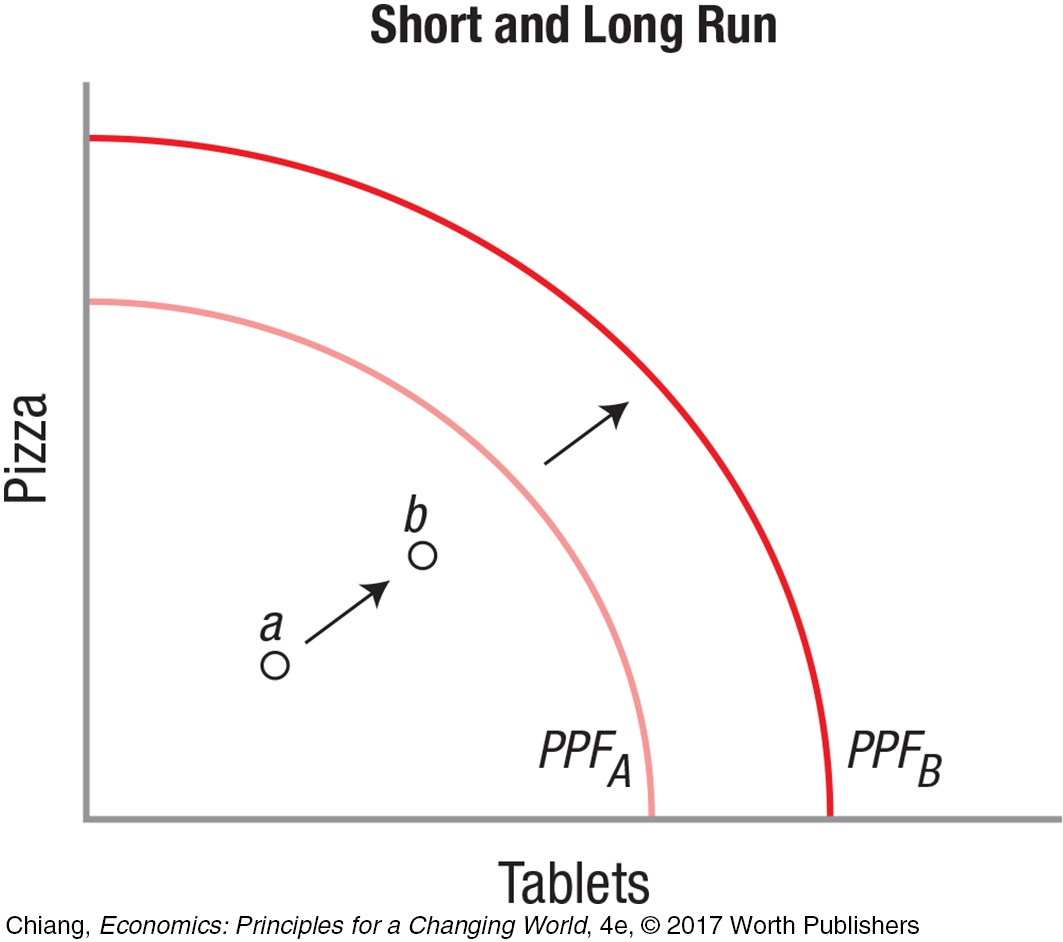
Section 2 Thinking About Short-
7.4 Short-
Short-
Long-
7.5 Factors of Production
Land (N): Includes land and natural resources
Labor (L): Within labor is human capital (H), labor improved by education or training
Capital (K): Manufactured goods used in the production process
Entrepreneurial ability (A): Includes ideas and the technology that is developed

Section 3 Applying the Production Function: Achieving Economic Growth
7.6 Productivity is the ability to turn a fixed amount of inputs (factors of production) into more outputs (goods and services).
Ways to Increase Productivity
Increasing access to natural resources
Improving quality of labor (human capital)
Increasing the capital-
to- labor ratio Promoting innovation and technology

7.7 Total factor productivity is a measurement of productivity taking into account all other factors beyond the quantity and quality of inputs that could influence production. Examples include natural disasters, climate, or cultural norms that influence the effectiveness of productive inputs.
Section 4 The Role of Government in Promoting Economic Growth
7.8 Government involvement in promoting economic growth occurs by way of investing in physical capital, human capital, and technology.
Physical capital: The building and maintenance of the country’s public capital (infrastructure), which includes roads, bridges, airports, power plants, and telecommunications networks
Human capital: Providing subsidized public college education, financial aid grants, and loans
Technology: Funding research via grants and the establishment of major government research labs


7.9 Government as a Guarantor of Economic Growth
Enforcement of contracts: A strong legal system
Protection of property rights: Ensuring that monetary rewards are provided to innovators
Stable financial system: A functioning and stable monetary system ensures investment is undertaken when the opportunity arises
Promoting free and competitive markets: International trade allows for specialization and gains from trade, and competitive markets ensure firms do not exploit market power, their ability to set prices for goods and services in a market