FIGURE 2 A SMALL NETWORK WITH FIXED CAPACITY
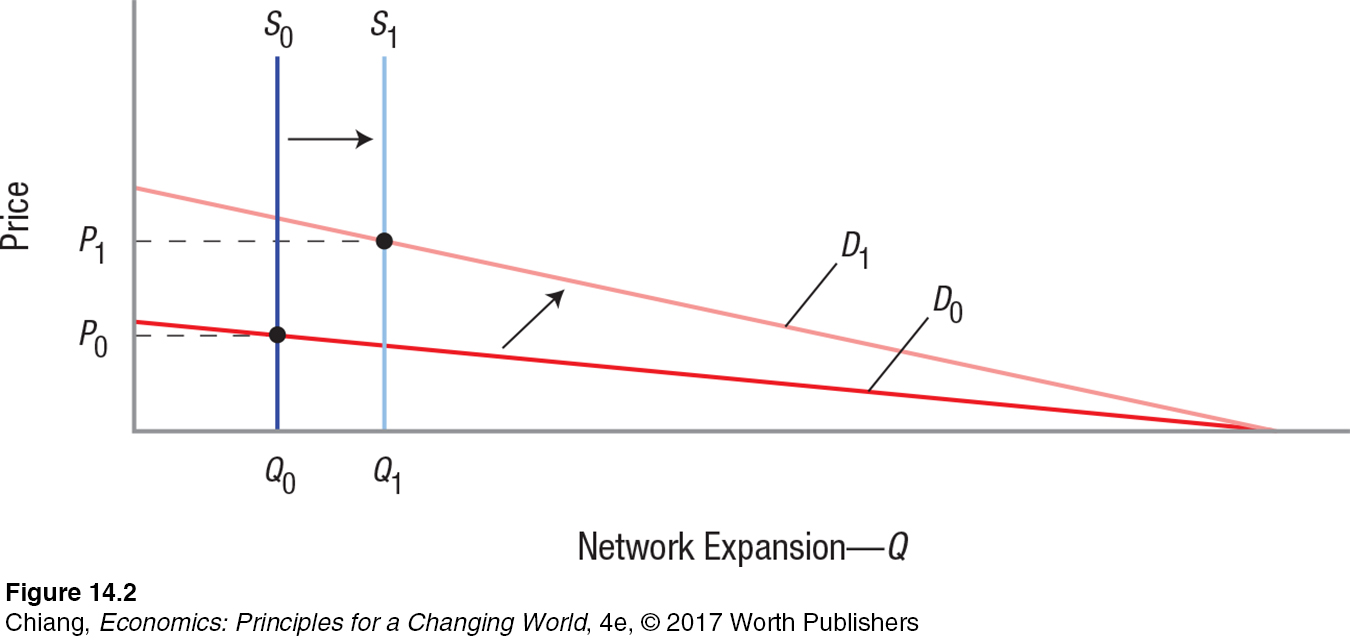 A small network has a fixed capacity of Q0, resulting in a vertical supply curve, S0. The intersection of S0 and D0 results in an equilibrium price of P0. As the network expands to S1, the value to existing and new users increases due to network effects, causing the demand curve to pivot to D1. The intersection of S1 and D1 leads to a higher equilibrium price of P1. This differs from a market for a no
A small network has a fixed capacity of Q0, resulting in a vertical supply curve, S0. The intersection of S0 and D0 results in an equilibrium price of P0. As the network expands to S1, the value to existing and new users increases due to network effects, causing the demand curve to pivot to D1. The intersection of S1 and D1 leads to a higher equilibrium price of P1. This differs from a market for a no[Leave] [Close]