FIGURE 6 EFFECTS OF A TARIFF
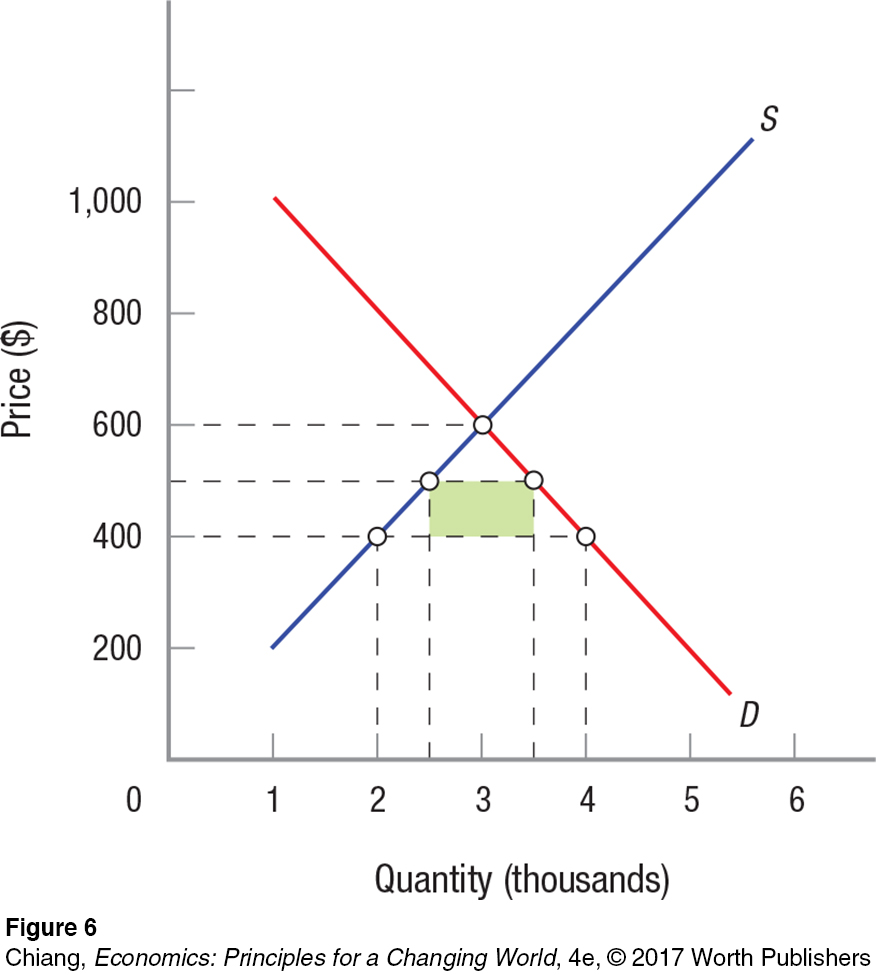 What are the effects of a typical tariff? Supply and demand curves S and D represent domestic supply and demand. Assume the product’s world price of $400 is lower than its domestic price. Imports will therefore be 2,000 units. If the country imposes a tariff of $100 on this product, the domestic price rises to $500, and imports fall to 1,000 units. Domestic consumers now buy less of the product at higher prices. However, the domestic industry is happy because its prices and output have risen. Also, the government collects revenues equal to the shaded area.
What are the effects of a typical tariff? Supply and demand curves S and D represent domestic supply and demand. Assume the product’s world price of $400 is lower than its domestic price. Imports will therefore be 2,000 units. If the country imposes a tariff of $100 on this product, the domestic price rises to $500, and imports fall to 1,000 units. Domestic consumers now buy less of the product at higher prices. However, the domestic industry is happy because its prices and output have risen. Also, the government collects revenues equal to the shaded area.[Leave] [Close]