QUESTIONS AND PROBLEMS
Check Your Understanding
Question 14.1
1. What is a network externality and how does it differ from a typical externality?
Question 14.2
2. Explain why a network demand curve slopes upward for small quantities.
Question 14.3
3. List three strategies a firm can use to segment its market for a network good.
Question 14.4
4. True or false: Once a firm’s network good becomes the market leader, it is extremely unlikely for the firm to lose that position within a five-
Question 14.5
5. Why does the 3D printer industry exhibit large economies of scale? Would there also be network externalities in the consumption of 3D printers? Explain.
Question 14.6
6. When one mails a letter to a foreign destination, what are the essential facilities involved and why is interconnection needed?
Apply the Concepts
Question 14.7
7. Suppose that two community organizations each plan their own public beach volleyball tournament on the same day at the same beach. Each organization wishes to have as many participants as possible. Further, a larger tournament is more fun for the participants. Suppose that a team consists of four players and at least four teams are required to hold a tournament. Explain what the tipping point would be and why a vicious cycle can develop if that number fails to be achieved.
Question 14.8
8. If a person decides to unsubscribe from a popular social network, it decreases the value of the network to everyone else. Why wouldn’t this action be considered a negative externality?
Question 14.9
9. Suppose that expansion of the productive capacity of a firm producing a network good reduces the average cost due to economies of scale, but generates a very large increase in demand due to the network effect. Is this good likely to be on the upward-
Question 14.10
10. Suppose that a new Harry Potter book called The Untold Stories of Harry Potter is released for sale, and fans line up for days to be the first to buy it. Are these fans core users or casual users in their demand for the new book? How could the book publisher maximize its profit using intertemporal pricing?
Question 14.11
11. Suppose that your bank opens up a dozen more automatic teller machines (ATMs) throughout the city, making it much easier to find one. What happens to the demand and supply curves for this network as it expands?
Question 14.12
12. Whenever a new car with satellite radio capability is purchased, the buyer is typically offered a free 90-
In the News
Question 14.13
13. When Google Apps launched almost a decade ago, it revolutionized the software industry. No longer was software confined to a single computer. Instead, apps are stored online allowing users to access documents and spreadsheets wherever they go. Google’s market dominance did not last forever, as Microsoft’s Office 365’s market share surpassed Google’s in 2015. What were some advantages of Office 365 that allowed it to gain market share so quickly against a market leader? When Google responded by eliminating fees by Office 365 users to switch to Google Apps, what strategy was Google employing?
Question 14.14
14. Internet interconnection has become an important issue as countries improve their network infrastructure. According to the International Charging Arrangements for Internet Services (ICAIS) agreement, countries wishing to access U.S. Web sites or use U.S. backbones (Internet networks) must pay the full cost of interconnection (as opposed to, say, telephone interconnection, where each side shares the cost). Why would a country agree to this type of arrangement in the first place (in the 1990s), and what developments have taken place since then that would cause them to now oppose this arrangement?
Solving Problems
WORK IT OUT  | interactive activity
| interactive activity
Question 14.15
15. Suppose Caroline values video game X at $70 and video game Y at $30, whereas Jacqueline values video game X at $30 and video game Y at $60. The marginal cost to produce each game is $0. If a firm that produces both games decides to bundle X and Y, what price should it charge, and why is this bundling strategy more profitable than selling each game separately at a single price (assuming price discrimination is not possible)?
Question 14.16
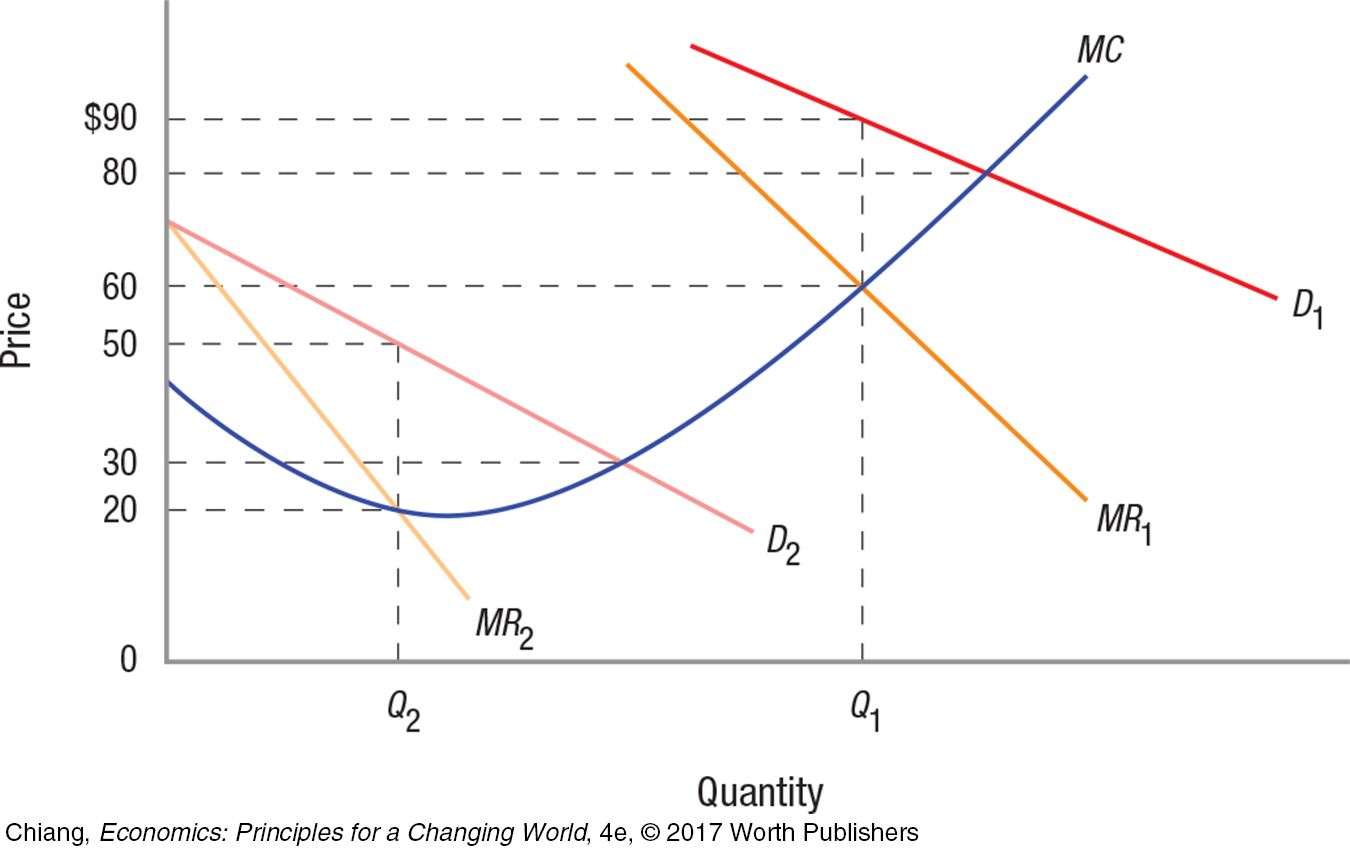
16. The accompanying figure shows two demand curves for ski lift tickets, one representing demand during February (peak season) and the other for April (low season). If the ski resort wishes to maximize its profit using peak-
 USING THE NUMBERS
USING THE NUMBERS
Question 14.17
17. According to By the Numbers, in what month and year did Uber surpass taxi services as the most popular form of local transportation? How much did Uber’s market share increase from the beginning of 2014 to the end of 2015?
Question 14.18
18. Compare the growth in Airbnb home-