QUESTIONS AND PROBLEMS
Check Your Understanding
Question 7.1
1. What is the difference between explicit and implicit costs? What is the difference between economic and accounting profits? Are these four concepts related? How?
Question 7.2
2. Why should sunk costs be ignored for decision making?
Question 7.3
3. How does the short run differ from the long run? Is the long run the same for all industries? Why or why not?
Question 7.4
4. Why should a firm never hire a worker when negative marginal returns set in?
Question 7.5
5. Why is the average fixed cost curve not U-
Question 7.6
6. What is the difference between marginal cost and average total cost?
Apply the Concepts
Question 7.7
7. If you work hard building your business and end up earning zero economic profit for the year, would this be considered a failed business to an economist? Why or why not?
Question 7.8
8. In order to take this class, you had to pay tuition, buy the textbook, and buy a new laptop. Which of these items (if any) would be considered a sunk cost? Explain your reasoning.
Question 7.9
9. The movie industry earns a substantial portion of its total revenues through Internet streaming and downloads. Although producing a movie can costs tens of millions of dollars, the marginal cost of producing another copy or download is practically nothing. For this industry, would short-
Question 7.10
10. List some of the reasons why the long-
Question 7.11
11. The Finger Lakes region in New York State produces wine. The climate favors white wines, but reds have been produced successfully in the past 15 years. Categorize the following costs incurred by one winery as either fixed or variable:
the capital used to buy 60 acres of land on Lake Seneca
the machine used to pick some varieties of grapes at the end of August and the beginning of September
the salary of the chief vintner, who is employed year-
round the wages paid to workers who bind the grape plants, usually in April, and usually over a period of 3 to 4 days
the wages paid to the same workers who pick the grapes at the end of August or early September
Page 191the costs of the chemicals sprayed on the grapes in July
the wages of the wine expert who blends the wine in August and September, after the grapes have been picked
the cost of the building where wine tastings take place from April to October
the cost of the wine used in the wine tasting
Question 7.12
12. If marginal cost is less than average total cost, are average total costs rising or falling? Alternatively, if marginal cost is more than average total cost, are average total costs rising or falling? Explain how this example might apply to a basketball player attempting to achieve a high average points per game.
In The News
Question 7.13
13. Fracking is the process by which oil is extracted from underground using a high-
Question 7.14
14. Colorado was the first state to legalize recreational marijuana in 2012. Since then, several states have followed, leading to a boom in the number of growers and shops selling marijuana. A problem, however, is that federal law still prohibits the sale of marijuana, though in practice state laws have been respected. Still, many shop owners choose to conduct transactions only in cash to avoid leaving an evidence trail from credit card transactions, which reduces the risk of prosecution but raises the risk of theft or loss. With so much retail competition along with added risk, why do many choose to venture into this business?
Solving Problems
Question 7.15
15. Suppose you pay $10 to watch a movie at the local cineplex, and afterward you sneak into the next theater to watch a second movie without paying. What is your marginal cost of watching the second movie? What is the average cost of watching the two movies? After the movies, you go to the batting cages and stand in for two rounds of pitches, each round costing $2. What is your marginal cost of batting the second round? What is the average cost of batting two rounds?
WORK IT OUT  | interactive activity
| interactive activity
Question 7.16
16. Using the following table, answer the following questions.
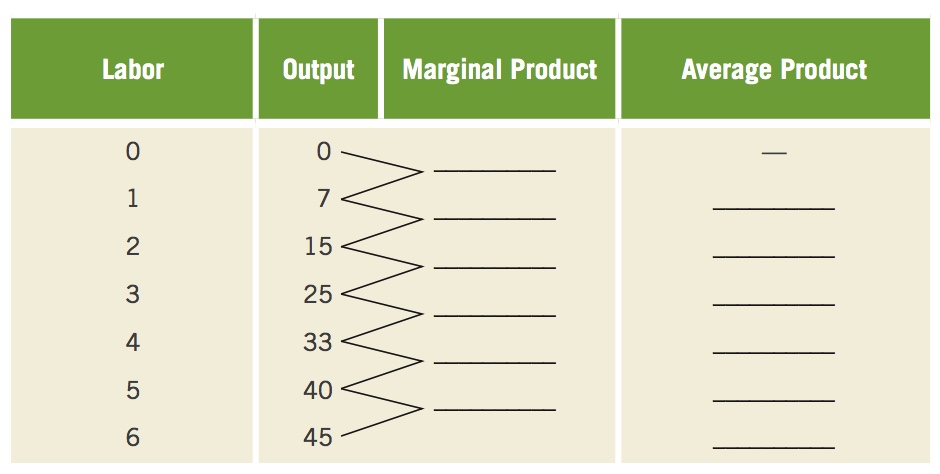
Complete the table, filling in the answers for marginal and average products.
Over how many workers is the firm enjoying increasing returns?
At what number of workers do diminishing returns set in?
Are negative returns shown in the table?
 USING THE NUMBERS
USING THE NUMBERS
Question 7.17
17. According to By the Numbers, explain why a correlation exists between the costs of industrial robots and the productivity rate over the last 20 years.
Question 7.18
18. According to By the Numbers, between which 5 years from 2000 to 2015 did Internet flight bookings increase the most (by percentage of overall sales)? Between which 5 years from 2000 to 2015 did Internet flight check-