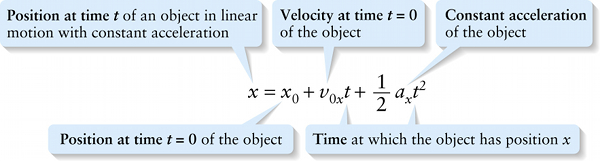
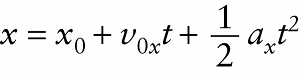Position, acceleration, and time for constant accelaration only (2-9)
Question 1 of 5
Question
Time at which the object has position x
{"title":"position at time t","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"1,21,21,53\"}]"} {"title":"position at time 0","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#993300","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"52,21,74,54\"}]"} {"title":"velocity at time 0","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#333300","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"119,24,139,55\"}]"} {"title":"constant acceleration","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#000080","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"246,22,265,47\"}]"} {"title":"Time at position x","description":"Correct!","type":"correct","color":"#333333","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"273,19,291,51\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"159,19,179,53\"}]"}Review
If we know the object’s initial position x_0, its initial velocity v_{0x}, and its constant acceleration a_x, Equation 2-9 tells us its position x at any time t.