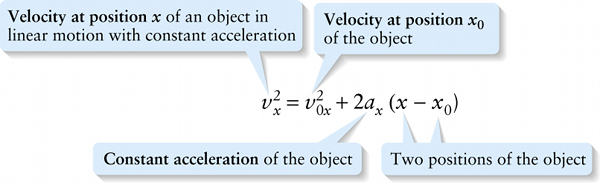
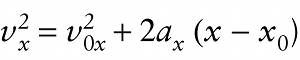Velocity, acceleration, and position for constant acceleration only (2-11)
Question 1 of 4
Question
Two positions of the object
{"title":"Velocity at x","description":"Correct","type":"incorrect","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"1,19,22,56\"}]"} {"title":"Velocity at position x0","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#993300","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"56,19,90,50\"}]"} {"title":"Constant acceleration","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#333300","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"150,21,177,45\"}]"} {"title":"Position of the two objects","description":"Correct!","type":"correct","color":"#000080","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"253,24,283,46\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"200,23,226,45\"}]"}Review
This equation expresses the object’s velocity when the object is at a given x coordinate, without reference to time.