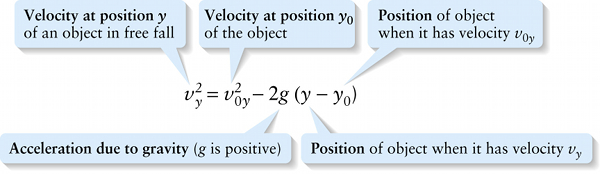
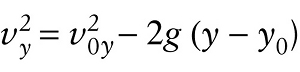Velocity, acceleration, and position for free fall (2-15)
Question 1 of 5
Question
Velocity at position \boldsymbol{y_0} of the object
{"title":"velocity at position y","description":"Incorrect","type":"correct","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"1,20,28,48\"}]"} {"title":"velocity at position y sub 0","description":"Correct!","type":"correct","color":"#ffcc00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"61,19,86,54\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"71,54,71,65\"}]"} {"title":"Acceleration due to gravity","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#333300","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"161,23,187,54\"}]"} {"title":"position of object when it has velocity v sub y","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#000080","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"198,22,218,52\"}]"} {"title":"position of object when it has velocity v sub 0y","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#333333","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"256,23,276,54\"}]"}Review
Note the minus sign in front of each term containing g, which is a reminder that the acceleration is always downward, in the negative y direction. If a freely falling object is rising, it slows down; if the object is descending, it speeds up.