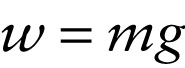Weight of an object of mass M (4-5)
Question 1 of 3
Question
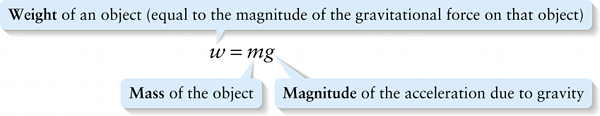
Weight of an object (equal to the magnitude of the gravitational force on that object)
{"title":"Weight of an object (equal to the magnitude of the gravitational force on that object)","description":"Correct!","type":"correct","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"1,13,47,59\"},{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"82,133\"}]"} {"title":"mass of the object","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#ffcc00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"118,11,119,13\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"107,19,153,52\"}]"} {"title":"Magnitude of the acceleration due to gravity","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#333300","code":"[{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"113,132\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"155,22,183,63\"}]"}Review
We know from Section 2-7 that if only gravity acts on an object, the object’s acceleration has magnitude g. So, we get the following expression for the weight of an object of mass m.