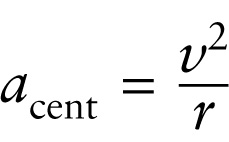Centripetal acceleration (5-10)
Question 1 of 3
Question
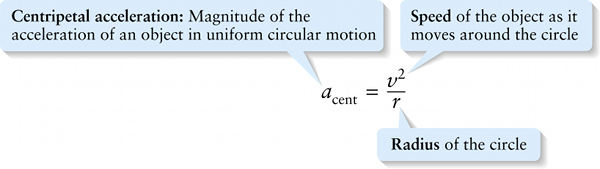
Centripetal acceleration: Magnitude of the acceleration of an object in uniform circular motion
{"title":"Centripetal acceleration: Magnitude of the acceleration of an object in uniform circular motion","description":"Correct!","type":"correct","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"82,133\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"2,74,26,108\"}]"} {"title":"Speed of the object as it moves around the circle","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#ffcc00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"118,11,119,13\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"178,39,206,77\"}]"} {"title":"Radius of the circle","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#333300","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"193,95,219,133\"}]"}Review
One of the simplest situations in which an object follows a curved trajectory is uniform circular motion, or motion around a circular path at a constant speed. We saw in Section 3-8 that in uniform circular motion, the acceleration at any point around the circle is directed toward the center of the circle (that is, it is centripetal) and has a magnitude acent that depends on the object’s speed v and the radius r of the circle: