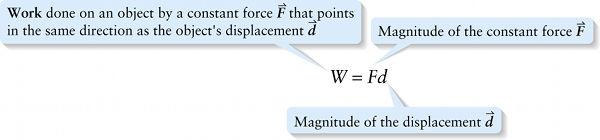
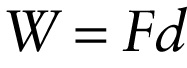Work done by a constant force that points in the same direction as straight-line displacements (6-1)
Question 1 of 3
Question
Magnitude of the displacement \boldsymbol{\vec{d}}
{"title":"Work done an object by a constant force vector F that points in the same direction as the object's displacement vector d","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"82,133\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"6,3,68,56\"}]"} {"title":"Magnitude of the constant force vector F","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#ffcc00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"118,11,119,13\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"120,2,156,59\"}]"} {"title":"Magnitude of the displacement vector d","description":"Correct!","type":"correct","color":"#333300","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"157,8,187,60\"}]"}Review
Suppose a constant force \vec{F} acts on an object as it moves through a straight-line displacement \vec{d}, and the force \vec{F} is in the same direction as \vec{d}. Then the work done by the force equals the product of the force magnitude F and the distance d over which the object moves: