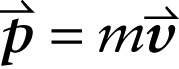Linear momentum (7-5)
Question 1 of 3
Question
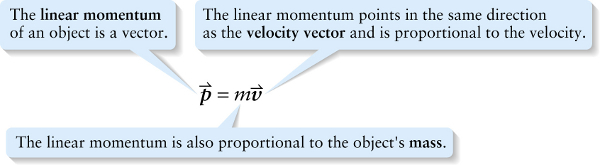
The linear momentum points in the same direction as the velocity vector and is proportional to the velocity.
{"title":"The linear momentum of an object is a vector","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"1,2,37,67\"},{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"82,133\"}]"} {"title":"The linear momentum points in the same direction as the velocity vector and is proportional to the velocity.","description":"Correct!","type":"correct","color":"#ffcc00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"143,9,182,52\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"118,11,119,13\"}]"} {"title":"The linear momentum is also proportional to the object's mass.","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#333300","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"98,23,139,55\"},{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"113,132\"}]"}Review
Our analysis of the skateboard problem, and especially Equation 7-3, suggests that it’s worthwhile to think about a quantity that’s equal to the product of an object’s mass m and its velocity vector →v. We’ll call this quantity the object’s linear momentum.