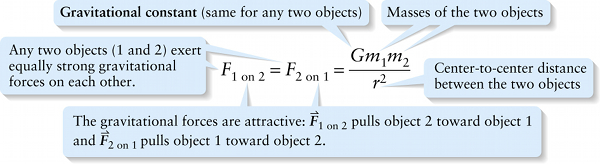
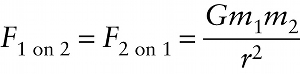Newton's law of universal gravitation (10-2)
Question 1 of 5
Question
Center-to-center distance between the two objects
{"title":"Any two objects exert equally strong gravitational forces on each \perpher.","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"1,23,28,63\"},{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"82,133\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"102,19,133,60\"}]"} {"title":"Gravitational constant (same for any two objects)","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#ffcc00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"118,11,119,13\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"201,1,230,32\"}]"} {"title":"Masses of the two objects","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#333300","code":"[{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"113,132\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"263,4,289,30\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"231,3,253,33\"}]"} {"title":"Center-to-center distance between the two objects","description":"Correct!","type":"correct","color":"#000080","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"235,52,255,73\"}]"} {"title":"The gravitational forces are attractive: vector F sub 1 on 2 pulls object 2 toward object 1 and vector F sub 2 on 1 pulls object 1 toward object 2.","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#333333","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"32,40,56,59\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"134,42,156,61\"}]"}Review
For the force of Earth on the Moon, m2 is the Moon’s mass and r is the Earth-Moon distance. If Equation 10-1 is true for any two objects, then it must also be true that the object of mass m2 exerts a gravitational force on the object of mass m1, and this force is directly proportional to the mass m1. But Newton’s third law (Section 4-5) tells us that the forces that the two objects exert on each \perpher have opposite directions and the same magnitude: F2 on 1=F1 on 2. Hence the gravitational force that each object exerts on the \perpher must be directly proportional to both m1 and m2. This chain of reasoning leads us to Newton’s law of universal gravitation: