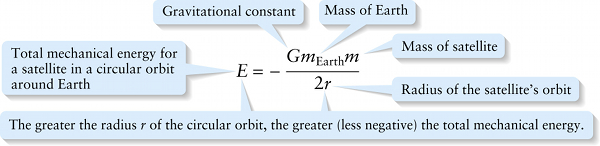
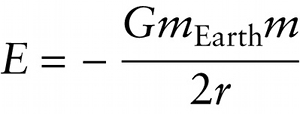Total mechanical energy for circular orbit (10-13)
Question 1 of 6
Question
Radius of the satellite's orbit
{"title":"Total mechanical energy for a satellite in a circular orbit around Earth","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"82,133\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"1,40,28,75\"}]"} {"title":"Gravitational constant","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#ffcc00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"118,11,119,13\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"122,3,155,40\"}]"} {"title":"Mass of Earth","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#333300","code":"[{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"113,132\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"195,33,199,34\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"158,15,196,39\"}]"} {"title":"Mass of satellite","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#000080","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"263,14,285,44\"}]"} {"title":"Radius of the satellite's orbit","description":"Correct!","type":"correct","color":"#333333","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"212,82,234,106\"}]"} {"title":"The greater the radius r of the circular orbit, the greater (less negative) the total mechanical energy.","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#800000","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"210,80,241,108\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"2,38,35,75\"}]"}Review
As we discussed in Section 10-3, the gravitational potential energy is negative. Making the orbital radius r larger makes the gravitational potential energy less negative—that is, closer to zero—which means that the gravitational potential energy increases. The total mechanical energy is the sum of K and Ugrav:
E=K+Ugrav=12mv2+(−GmEarthmr)=GmEarthm2r+(−GmEarthmr)
or: