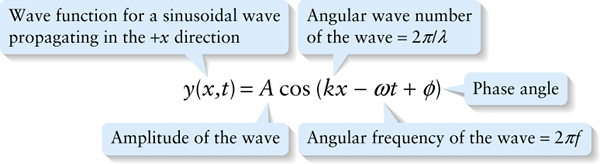
Chapter 13. Wave function for a sinusoidal wave propagating in the +x direction (13-6)
Question
75Sbgb9zyWwrUoz/JUa3oEoaYDFHnBh0pPYS5K/xYeSkAT6U1NIuebYVwu2SV/zzAzkW2w6Ud7RFheLpJSym8O0yaPOxy69GWpG0Iw==Question
yPycVM3E5gD3aMUfiJ8lui7tDo7UOhP4Dl3iESMIOcIZ3ZHo4U0dDVD4mpvG4vOjQhNqjCRQqbs=Question
BSm/p8ry4dYXtQ3h1a9oSg==Question
d6HYmM9PCuRly8U45YA3yj5mAmM8IAsZIatkXHPQ/S+cAjwKyaWhETKgjGWud1rNQuestion
jgsMRhUpiW7jFvmHQSbmgVK6asrJrCBreZ9vNQ==Review
Since \(2\pi\) represents the number of radians in one cycle and wavelength \(\lambda\) is in meters, the angular wave number \(k\) is measured in radians per meter (rad/m). We use the adjective \(\textit{angular}\) since the term "wave number" is typically used for \(1/\lambda\), the reciprocal of the wavelength. This quantity multiplied by \(2\pi\) is the angular wave number \(k = 2\pi{f}\).
In terms of angular wave number, we can rewrite Equation 13-4 as