Temperature and average translational kinetic energy of an ideal gas molecule (14-13)
Question 1 of 5
Question
Temperature of the gas on the Kelvin scale
{"title":"Average translational kinetic energy of a molecule in an ideal gas","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"82,133\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"10,16,12,16\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"2,11,11,26\"}]"} {"title":"Average value of the square of a gas molecule’s speed","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#ffcc00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"184,10,194,27\"}]"} {"title":"Temperature of the gas on the Kelvin scale","description":"Correct!","type":"correct","color":"#333300","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"287,9,300,25\"}]"} {"title":"Boltzmann constant","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#000080","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"277,10,287,27\"}]"} {"title":"Mass of a single gas molecule","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#333333","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"166,14,181,27\"}]"}Review
We can learn something no less important by comparing Equation 14-12 with the ideal gas law in terms of number of molecules, Equation 14-6: pV=NkT, or p=(N/V)kT. In order for both Equations 14-6 and 14-12 to be correct, it must be true that (2/3)Ktranslational, average=kT, or
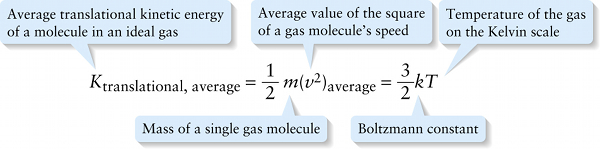
In words, Equation 14-13 says that the average translational kinetic energy of a molecule in an ideal gas is directly proportional to the Kelvin temperature of the gas. This justifies the statement we made in Section 14-2 about the physical meaning of temperature.