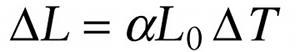Change in length due to a temperature change (14-18)
Question 1 of 4
Question
Coefficient of linear expansion of the substance of which the object is made
{"title":"Change in the length of an object","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"82,133\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"10,16,12,16\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"9,5,73,41\"}]"} {"title":"Length of the object before the temperature change","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#ffcc00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"157,6,182,42\"}]"} {"title":"Temperature change of the object that causes the length change","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#333300","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"213,5,282,43\"}]"} {"title":"Coefficient of linear expansion of the substance of which the object is made","description":"Correct!","type":"correct","color":"#000080","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"122,10,160,45\"}]"}Review
Experiment shows that if the temperature change Δt of a solid object is not too great, the change in each dimension of the object is proportional to Δt. In particular, if a solid object initially has length L0, the change ΔL in its length when the temperature changes by Δt is
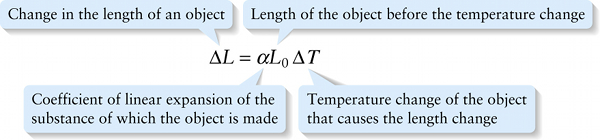
The quantity α (Greek letter alpha) in Equation 14-18 is called the coefficient of linear expansion. It depends on what the object is made of, but not on the shape or size of the object.