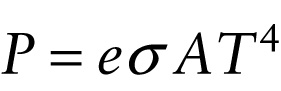Rate of energy flow in radiation (14-22)
Question 1 of 5
Question
Surface area of the object
{"title":"Rate at which an object emits energy in the form of radiation","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"82,133\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"10,16,12,16\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"2,26,40,79\"}]"} {"title":"Emissivity of the object (a number between 0 and 1)","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#ffcc00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"96,44,125,76\"}]"} {"title":"Temperature of the object on the Kelvin scale","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#333300","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"216,31,261,75\"}]"} {"title":"Surface area of the object","description":"Correct!","type":"correct","color":"#000080","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"173,30,214,77\"}]"} {"title":"Stefan-Boltzmann constant = 5.6704 × 10 ^ -8 W dot m ^ -2 dot K ^-4","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#333333","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"127,42,167,77\"}]"}Review
Experiment shows that any object emits energy in the form of radiation. The rate at which radiation is emitted by an object—that is, the radiated power P in joules per second or watts—is proportional to the object’s surface area A and to the fourth power of the Kelvin temperature T of the object:
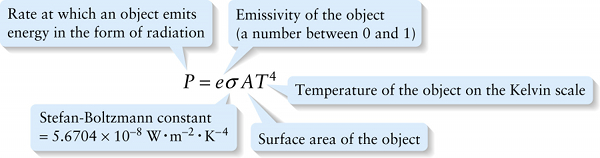
The Stefan-Boltzmann constant σ (the Greek letter sigma) has the same value for all objects. The quantity e is the emissivity of the surface; its value indicates how well or how poorly a surface radiates. A surface with a value of e close to 1 is a good radiator of thermal energy.