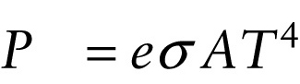Rate of energy flow in radiation (14-22)
Question
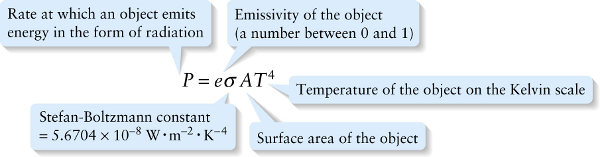
Surface area of the object
{"title":"Rate at which an object emits energy in the form of radiation","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"82,133\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"10,16,12,16\"},{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"144,22\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"1,25,35,70\"}]"} {"title":"Emissivity of the object (a number between 0 and 1)","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#ffff00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"129,41,157,71\"}]"} {"title":"Temperature of the object on the Kelvin scale","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#00ff00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"238,25,280,72\"}]"} {"title":"Surface area of the object","description":"Correct!","type":"correct","color":"#ff0000","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"200,28,239,72\"}]"} {"title":"Stefan-Boltzmann constant = 5.6704 × 10−8 W . m−2 . K−4","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#000080","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"159,39,198,72\"}]"}Review
The higher the temperature of an object of a given size, the greater the radiated power P and so the more brightly it glows.
Experiment also shows that the color of the radiation emitted by an object depends on its temperature T (Figure 26-4). A heated object emits light at all wavelengths, but emits most strongly at a particular frequency called the frequency of maximum emission. As the temperature increases, the frequency of maximum emission increases.
Equation 14-22 shows that the radiated power also depends on a quantity e called the emissivity, which depends on the properties of the object’s surface. This has its greatest value (e=1) for an idealized type of dense object called a blackbody. An ideal blackbody does not reflect any light at all, but absorbs all radiation falling on it.