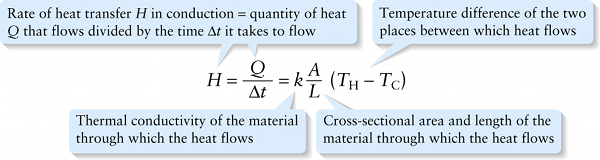
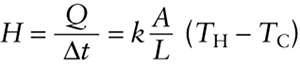Rate of energy flow in conduction (14-23)
Question 1 of 4
Question
Cross-sectional area and length of the material through which the heat flows
{"title":"Rate of heat transfer H in conduction = quantity of heat Q that flows divided by the time Delta t it takes to flow","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"82,133\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"10,16,12,16\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"1,20,27,47\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"54,3,98,63\"}]"} {"title":"Temperature difference of the two places between which heat flows","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#ffcc00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"192,17,292,51\"}]"} {"title":"Cross-sectional area and length of the material through which the heat flows","description":"Correct!","type":"correct","color":"#333300","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"149,6,171,64\"}]"} {"title":"Thermal conductivity of the material through which the heat flows","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#000080","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"128,20,146,48\"}]"}Review
Figure 14-20 shows an idealized situation in which conduction takes place. The cylinder of length L and cross-sectional area A is in thermal contact at one end with a hot region at temperature TH and in thermal contact at the other end with a cold region at temperature TC. Experiment shows that the rate of heat transfer is proportional to the temperature difference TH−TC (the greater the temperature difference, the more rapidly heat flows). The rate of heat trans- fer is also greater if the cylinder is short (L is small) and wide (A is large). We can put these observations together into a single equation: