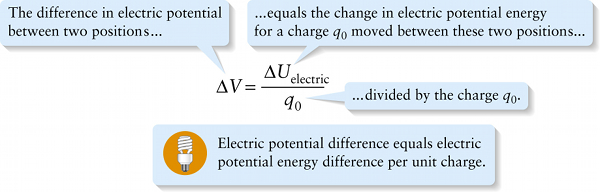
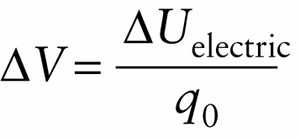Electric potential difference related to electric potential energy difference (17-6)
Question 1 of 3
Question
…divided by the charge q0.
{"title":"The difference in electric potential between two positions...","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"82,133\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"10,16,12,16\"},{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"144,22\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"31,40,69,85\"}]"} {"title":"…equals the change in electric potential energy for a charge q sub 0 moved between these two positions…","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#ffcc00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"157,2,195,50\"}]"} {"title":"…divided by the charge q sub 0.","description":"Correct!","type":"correct","color":"#333300","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"169,87,202,128\"}]"}Review
The key to understanding energy and power in electric circuits is that there is a potential difference across each circuit element, which means that a change takes place in electric potential energy when a moving charge traverses a circuit element. Remember from Section 17-3 the relationship between electric potential difference and electric potential energy difference: