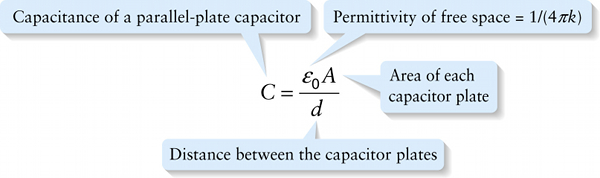
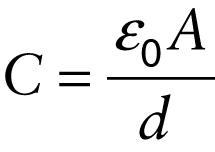Capacitance of a parallel-plate capacitor (17-13)
Question 1 of 4
Question
Area of each capacitor plate
{"title":"Capacitance of a parallel-plate capacitor","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"82,133\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"10,16,12,16\"},{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"144,22\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"5,52,46,96\"}]"} {"title":"Permittivity of free space = 1/(4pk)","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#ffcc00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"113,16,144,55\"}]"} {"title":"Area of each capacitor plate","description":"Correct!","type":"correct","color":"#333300","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"227,24,228,24\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"165,6,210,55\"}]"} {"title":"Distance between the capacitor plates","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#000080","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"134,91,179,141\"}]"}Review
For a parallel-plate capacitor, C depends only on the area A of the plates, the distance d between them, and the material between them. We’ve assumed that the plates are separated by vacuum; in Section 17-8 we’ll explore what happens if the space between the capacitor plates is filled with a different material. Capacitance is therefore a compact way to summarize the electrical properties of a capacitor. In particular, capacitance tells us the amount of charge that can be stored on a capacitor held at a given voltage.