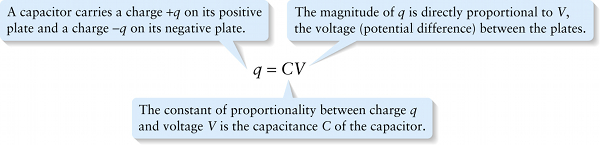
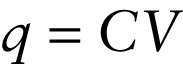Charge, voltage, and capacitance for a capacitor (17-14)
Question 1 of 3
Question
The constant of proportionality between charge q and voltage V is the capacitance C of the capacitor.
{"title":"A capacitor carries a charge +q on its positive plate and a charge −q on its negative plate.","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"82,133\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"10,16,12,16\"},{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"144,22\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"1,21,36,66\"}]"} {"title":"The magnitude of q is directly proportional to V, the voltage (potential difference) between the plates.","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#ffcc00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"145,6,182,54\"}]"} {"title":"The constant of proportionality between charge q and voltage V is the capacitance C of the capacitor.","description":"Correct!","type":"correct","color":"#333300","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"98,6,141,52\"}]"}Review
Let’s apply Kirchhoff's loop rule to the circuit shown in Figure 18-17b. In Section 17-5 we found that the magnitude of the charge q on the capacitor plates is proportional to the voltage V across the capacitor: