Electric field in an isolated parallel-plate capacitor with a dielectric (17-27)
Question 1 of 3
Question
Electric field in an isolated parallel-plate capacitor with dielectric between the plates
{"title":"Electric field in an isolated parallel-plate capacitor with dielectric between the plates","description":"Correct!","type":"correct","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"82,133\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"10,16,12,16\"},{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"144,22\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"2,47,40,100\"}]"} {"title":"Electric field in that same capacitor with no dielectric between the plates","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#ffcc00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"128,6,168,53\"}]"} {"title":"Dielectric constant: note that k ≥ 1","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#00ff00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"138,98,176,134\"}]"}Review
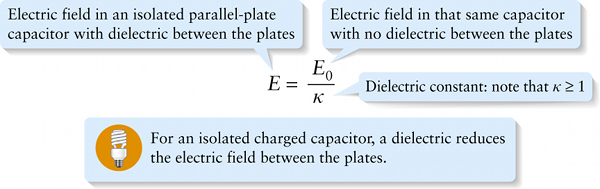
The quantity κ (the Greek letter kappa) is the dielectric constant of the material. The greater the value of κ, the more the dielectric is polarized when it is placed between the plates of a charged capacitor, so the greater the magnitude of the field →Edielectric due to the dielectric and the smaller the magnitude E of the net field. Table 17-1 lists values of the dielectric constant for a variety of materials.