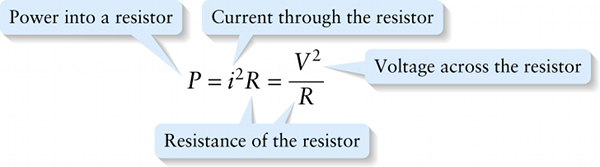
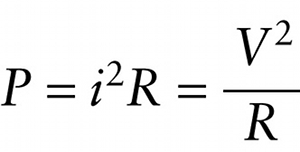Power for a resistor (18-24)
Question 1 of 4
Question
Voltage across the resistor
{"title":"Power into a resistor","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"82,133\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"10,16,12,16\"},{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"144,22\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"2,66,32,108\"}]"} {"title":"Current through the resistor","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#ffcc00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"89,65,106,109\"}]"} {"title":"Voltage across the resistor","description":"Correct!","type":"correct","color":"#333300","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"234,21,272,67\"}]"} {"title":"Resistance of the resistor","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#000080","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"242,100,285,147\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"127,65,163,110\"}]"}Review
For the special case where the circuit element is a resistor with resistance R, Equation 18-9 tells us that the voltage V across the resistor is equal to the product of the current and the resistance: V=iR, or equivalently i=V/R. We can use these two expressions to rewrite Equation 18-23 in two equivalent forms for the special case of a resistor:
P=i(iR) or P=(VR)V
We can simplify these to