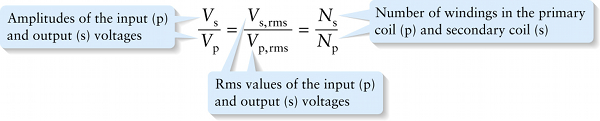
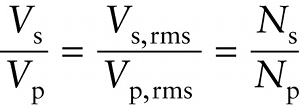Input and output voltages for a transformer (21-10)
Question 1 of 3
Question
Rms values of the input (p) and output (s) voltages
{"title":"Amplitudes of the input (p) and output (s) voltages","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"82,133\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"10,16,12,16\"},{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"144,22\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"5,3,36,35\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"5,58,35,91\"}]"} {"title":"Number of windings in the primary coil (p) and secondary coil (s)","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#ffcc00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"254,0,290,37\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"254,58,290,93\"}]"} {"title":"Rms values of the input (p) and output (s) voltages","description":"Correct!","type":"correct","color":"#333300","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"104,3,134,38\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"103,57,133,89\"}]"}Review
In other words, in a transformer the ratio of the number of windings in the secondary coil (Ns) to the number of windings in the primary coil (Np) determines the output voltage relative to the input voltage. In a step-up transformer, Ns is greater than Np, so the output voltage is greater than the input voltage. In a step-down transformer, Ns is less than Np, which results in an output voltage less than the input voltage.
.