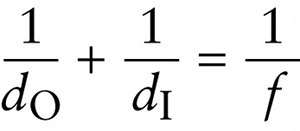Mirror equation and lens equation (24-11)
Question 1 of 3
Question
Focal length
{"title":"Object distance","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"82,133\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"10,16,12,16\"},{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"144,22\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"1,67,31,114\"}]"} {"title":"Focal length","description":"Correct!","type":"correct","color":"#ffff00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"259,67,291,124\"}]"} {"title":"Image distance","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#00ff00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"131,71,159,114\"}]"}Review
If we replace 2/r with 1/r in Equation 24-10, we get the final form of the mirror equation:
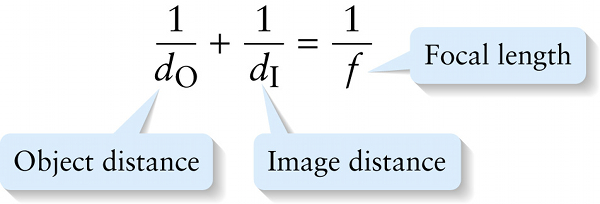
We also call Equation 24-11 the lens equation because, as we shall see in Section 24-8, it’s also applicable to the image formed by a lens.