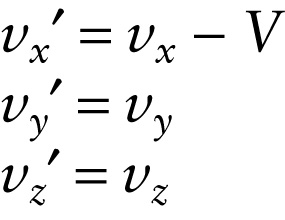Galilean velocity transformation (25-5)
Question
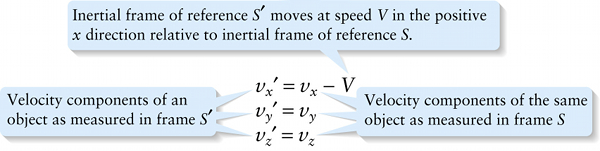
Velocity components of an object as measured in frame S′
{"title":"Inertial frame of reference S′ moves at speed V in the positive x direction relative to inertial frame of reference S.","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"82,133\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"10,16,12,16\"},{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"144,22\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"243,4,285,57\"}]"} {"title":"Velocity components of the same object as measured in frame S","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#ffff00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"127,21,157,56\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"123,88,155,125\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"120,158,152,199\"}]"} {"title":"Velocity components of an object as measured in frame S′","description":"Correct!","type":"correct","color":"#00ff00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"1,22,34,56\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"1,92,33,126\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"2,158,28,197\"}]"}Review
Equations 25-5, which relate the velocity of an object in frame S′ to the velocity of the same object in frame S, are called the Galilean velocity transformation.
As an example, think again of the ball shown in Figure 25-5. If the ball moves straight up and down as measured in frame S′, then in that frame the ball is in free fall with only a ycomponent of velocity. The other two components The other two components are zero: v′x=v′z=0. As measured in frame S, the velocity of the ball has component
vx=v′x+V=Vvy=v′yvz=v′z=0
As measured in frame S, the ball moves up and down along the y direction with the same velocity as measured in frame S′:vy=v′y. At the same time, as measured in frame S the ball maintains a constant velocity V in the x direction. That’s just the behavior we expect for a projectile: Its motion is a combination of up-and-down free fall and constant-velocity horizontal motion (see Section 3-6).