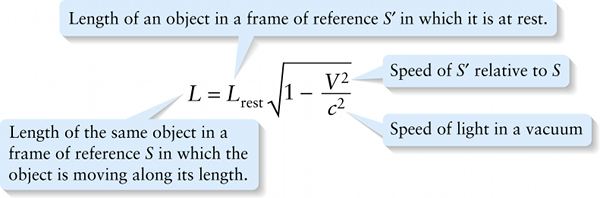
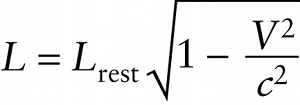Length contraction (25-14)
Question 1 of 4
Question
Length of the same object in a frame of reference S in which the object is moving along its length.
{"title":"Length of an object in a frame of reference S in which it is at rest.","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"82,133\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"10,16,12,16\"},{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"144,22\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"72,35,95,74\"}]"} {"title":"Speed of S′ relative to S","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#ffff00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"249,15,282,51\"}]"} {"title":"Speed of light in a vacuum","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#00ff00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"254,73,278,99\"}]"} {"title":"Length of the same object in a frame of reference S in which the object is moving along its length.","description":"Correct!","type":"correct","color":"#000080","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"1,38,25,74\"}]"}Review
If the rod is moving, V is greater than zero and the factor √1−V2/c2 is less than 1. So the length L of the moving rod is less than the length Lrest of the rod at rest. In other words, a moving object is shortened along the direction in which it is moving. This is called length contraction.