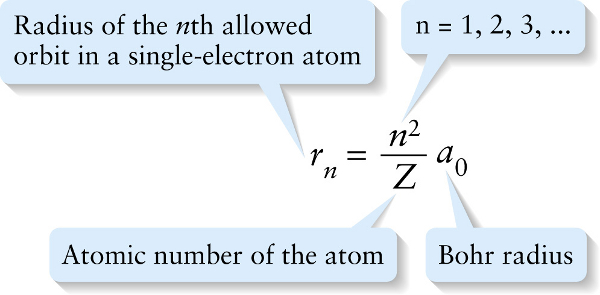
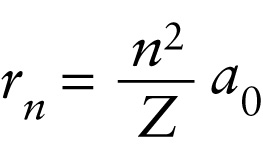Orbital radii in the Bohr model (26-23)
Question 1 of 4
Question
Radius of the nth allowed orbit in a single-electron atom
{"title":"Radius of the nth allowed orbit in a single-electron atom","description":"Correct!","type":"correct","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"82,133\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"10,16,12,16\"},{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"144,22\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"1,69,26,100\"}]"} {"title":"n = 1, 2, 3, ...","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#ffff00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"131,35,164,70\"}]"} {"title":"Bohr radius","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#00ff00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"212,65,241,93\"}]"} {"title":"Atomic number of the atom","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#ff0000","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"137,89,180,142\"}]"}Review
The integer n identifies the orbit, where the n=1 orbit is the closest to the nucleus. Because every element is distinguished by the number of protons it carries, the atomic number Z specifies a particular element. So, for example, setting Z equal to 1 gives the radii of the electron orbits in a hydrogen atom, and setting Z equal to 1 and n equal to 1 gives the radius of the first electron orbit in hydrogen.