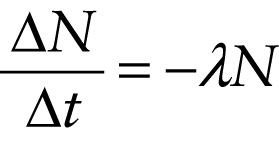Radioactive decay equation (27-4)
Question 1 of 4
Question
...and is proportional to the number of radioactive nuclei that remain.
{"title":"In a sample of radioactive material, the rate of change of the number of radioactive nuclei...","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"82,133\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"10,16,12,16\"},{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"144,22\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"45,5,96,55\"}]"} {"title":"... is negative because the number of nuclei decreases due to decay...","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#ffff00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"163,61,199,80\"}]"} {"title":"...and is proportional to the number of radioactive nuclei that remain.","description":"Correct!","type":"correct","color":"#00ff00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"233,43,277,88\"}]"} {"title":"...is proportional to the decay constant (the probability that a given nucleus decays in a one-second interval)...","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#ff6600","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"199,40,235,90\"}]"}Review
The minus sign in Equation 27-3 indicates that the number of nuclei decreases as a result of the decays. If we divide both sides of Equation 27-3 by the elapsed time Δt, we get an expression for the rate of change ΔN/Δt of the number of nuclei:
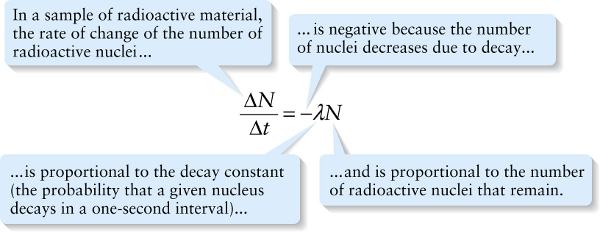
Equation 27-4 tells us that as time goes by, the decay rate will decrease because the number of radioactive nuclei will decrease. Using the tools of calculus, we can solve Equation 27-4 to find the number of nuclei present as a function of time, N(t).