Chapter 6. Language Areas in the Brain
Learning Objectives
side view of the brain with language areas highlighted
Locate the major brain areas in the left hemisphere that are involved in language.
Identify the basic functions of each brain area involved in language.
Review
Review
Select the NEXT button to continue with the Review.

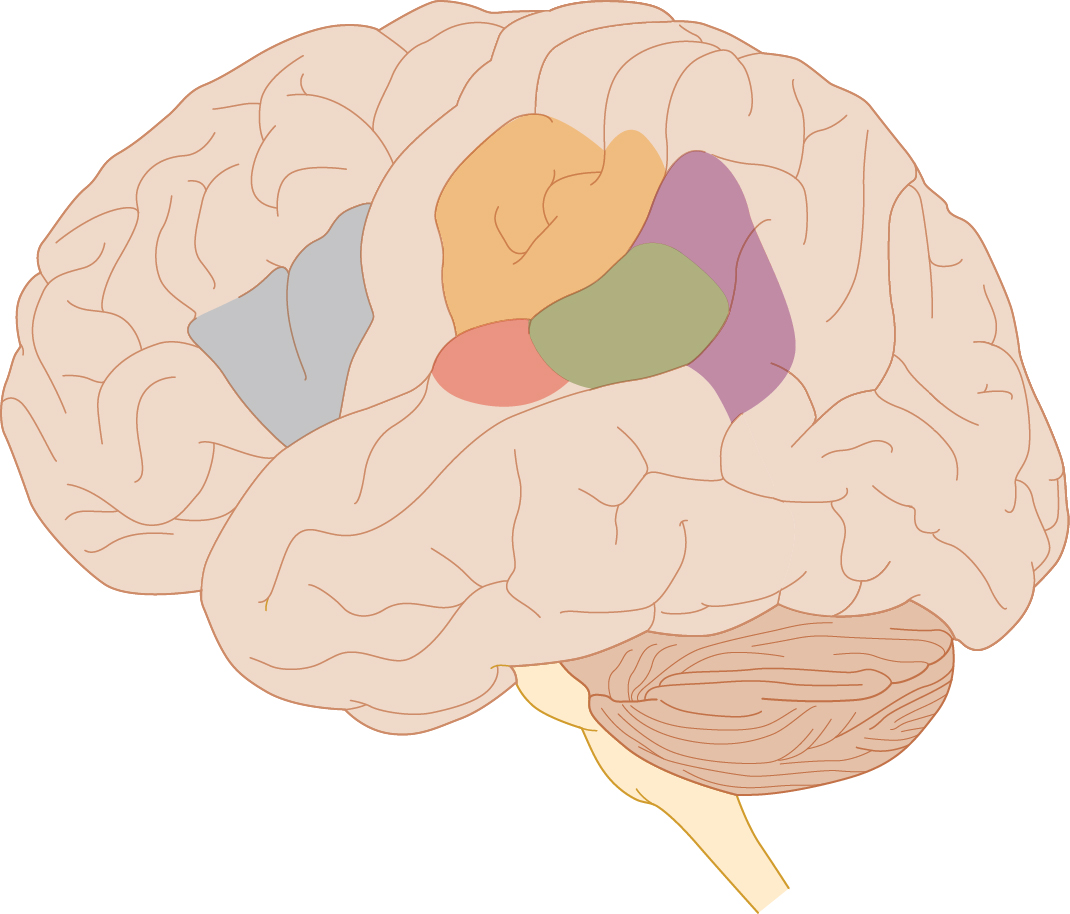
Diagram of the left hemisphere of the brain. The following structures are labeled: motor cortex, parietal lobe, Wernicke's area, angular gyrus, occipital lobe, visual cortex, cerebellum, temporal lobe, auditory cortex, Broca's area, frontal lobe.
1. Language involves several distinct areas in the brain (usually in the left hemisphere of the brain, as shown here).
Review
Review
Select the NEXT button to continue with the Review.

Diagram of the left hemisphere of the brain.
2. When a person is speaking, Broca’s area generates the speech code and sends those signals to the motor cortex, which moves the muscles of the mouth to produce speech sounds.
Review
Review
Select the NEXT button to continue with the Review.

Diagram of the left hemisphere of the brain.
3. When a person is listening to speech, the auditory cortex processes the sound waves and creates an auditory code. Wernicke’s area then interprets the auditory code as language.
Review
Review
Select the NEXT button to continue with the Review.

Diagram of the left hemisphere of the brain.
4. Two additional brain areas are involved when a person is reading. First, the visual cortex processes the printed words on a page to create a visual representation of each letter.
Review
Review
Select the NEXT button to continue with the Review.

Diagram of the left hemisphere of the brain.
5. Then the angular gyrus uses the output from the visual cortex to produce an auditory code that Wernicke’s area can understand.
Practice: Exploring Language Areas
Practice: Exploring Language Areas
Roll over each item and, for those that appear highlighted, see a brief description.
processes written words and creates visual representations
interprets auditory code as language
turns visual representations into an auditory code
moves mouth muscles to pronounce words
generates speech code and controls speech muscles via the motor cortex
processes sound waves and creates an auditory code

Diagram of the left hemisphere of the brain.
Quiz 1
Quiz 1
Drag each label to the line pointing to the appropriate structure. When all the labels have been placed, select the CHECK ANSWER button.

Diagram of the left hemisphere of the brain with labels removed.
Quiz 2
Quiz 2
Match the terms with their descriptions by dragging each colored circle to the appropriate gray circle. When all the circles have been placed, select the CHECK ANSWER button.
Conclusion
