Chapter 2. Context Influences Color
Learning Objectives

Understand the importance of context in color perception.
Describe the difference between color contrast and color constancy.
Review
Review
Select the NEXT button to continue with the Review.

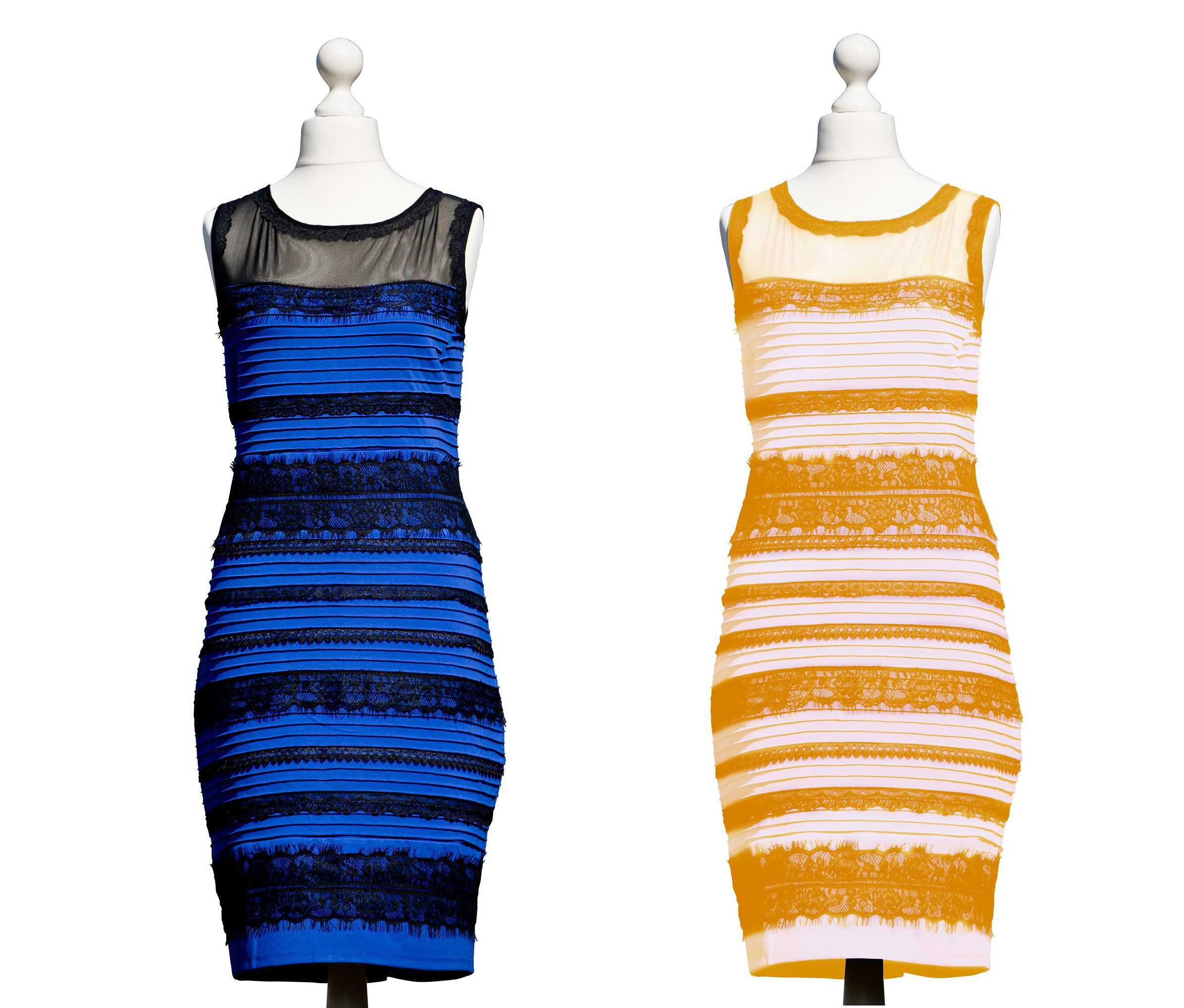
1. Our perception of the color of an object always depends on the surrounding colors.
2.0.1 Review
Review
Select the NEXT button to continue with the Review.

2. The neural connections within the retina of the eye and the visual cortex of the brain are designed to evaluate the light reflected from any object in comparison to the surrounding objects.
2.0.2 Review
Review
Select the NEXT button to continue with the Review.

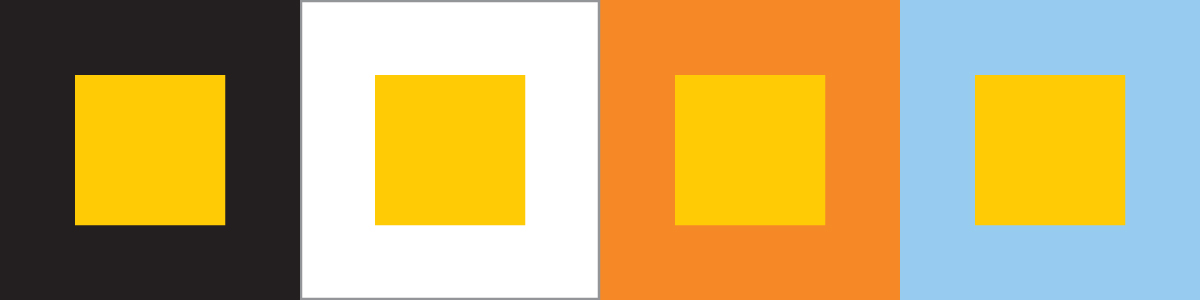
3. This comparison produces color contrast, and our perception of an object's color changes as the background color changes.
2.0.3 Review
Review
Select the NEXT button to continue with the Review.
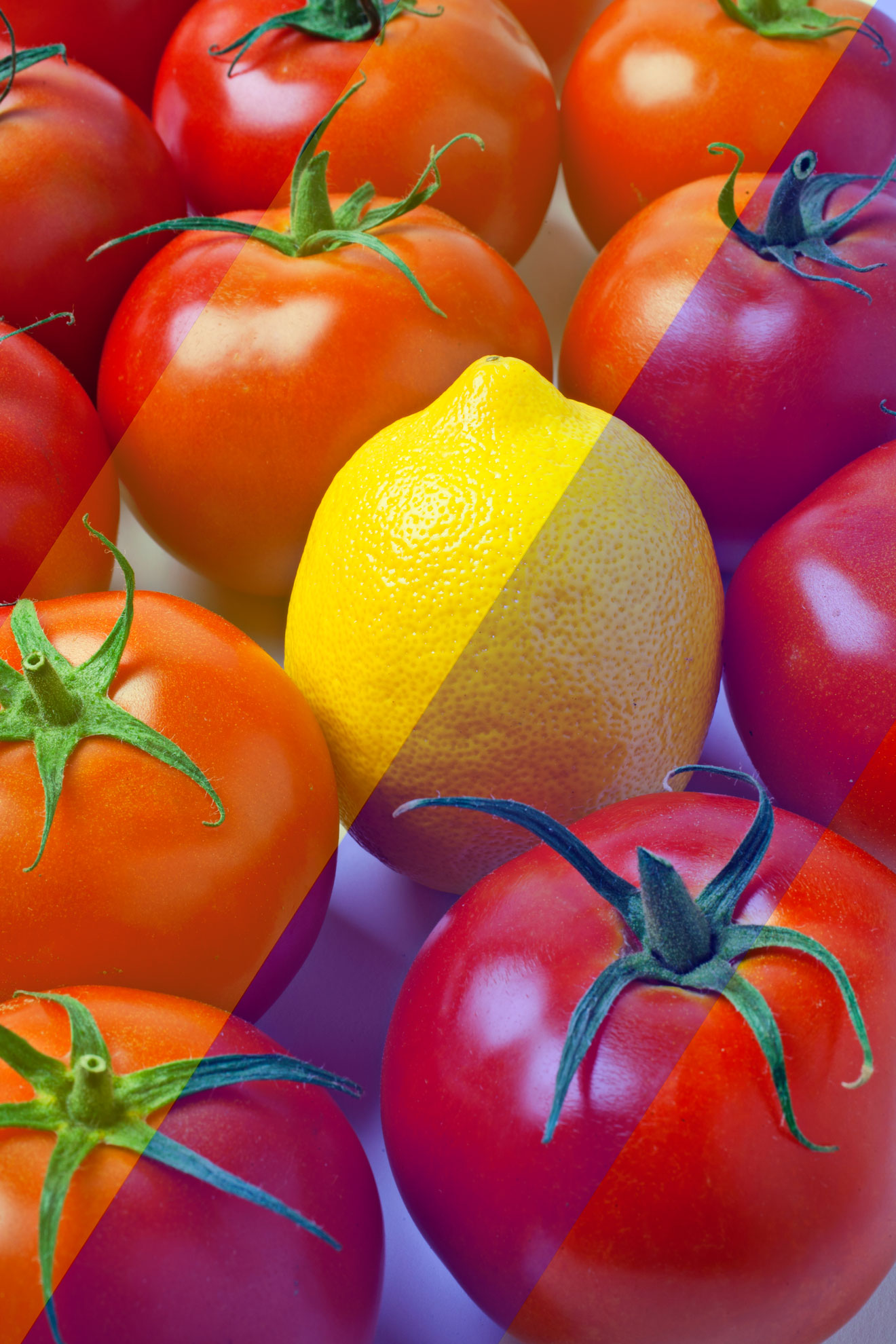


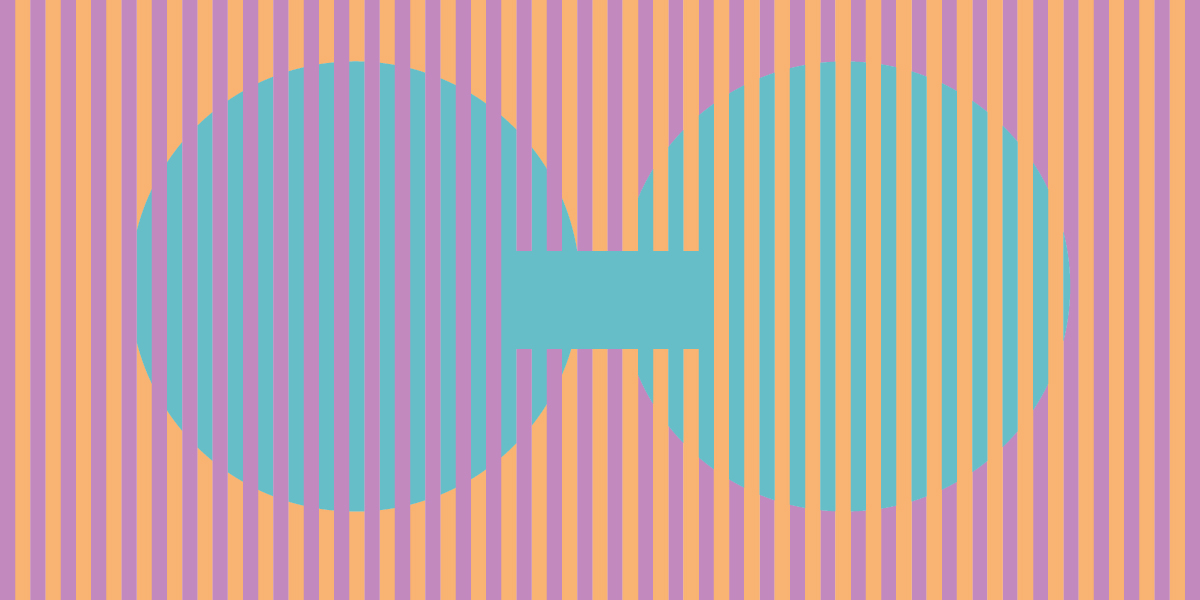
4. But this comparison also produces color constancy — allowing the perceived color of a familiar object to remain roughly the same even when the lighting changes.
2.0.4 Review
Review
Select the NEXT button to continue with the Review.


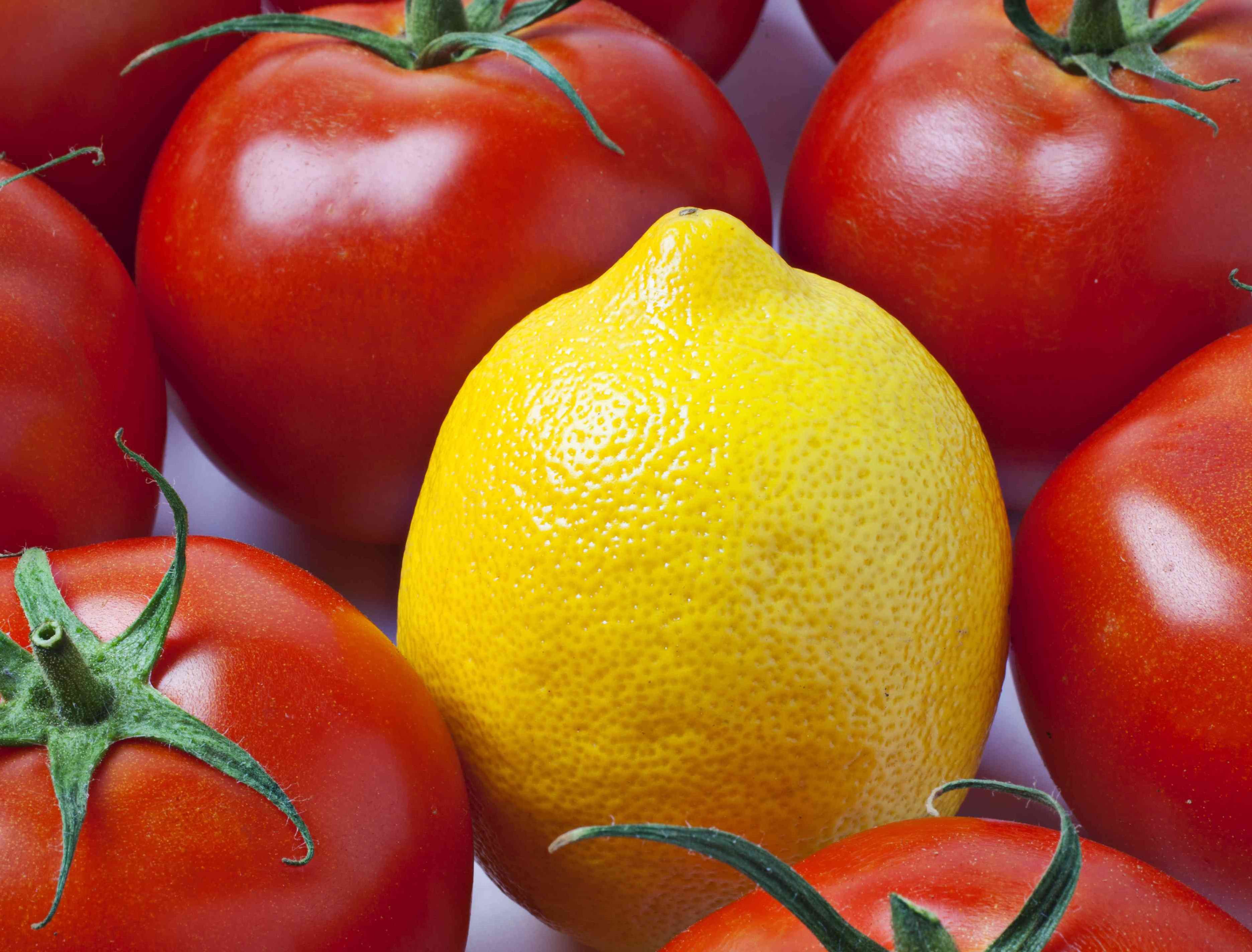
5. For example, if we are viewing a yellow lemon, we will continue to perceive the lemon as yellow even if the light falling on the lemon changes from white to blue or green, thus changing the wavelength of the light being reflected from the lemon's surface.
Practice 1: Demonstrating Color Contrast
Practice 1: Demonstrating Color Contrast
Use the buttons to vary the color of the circles and squares, and observe how the background color of the squares influences your perception of the color of the circles.
The principle of color contrast predicts that the perceived color of an object will change when the surrounding color changes. Try it!

Circles color:
Squares color:
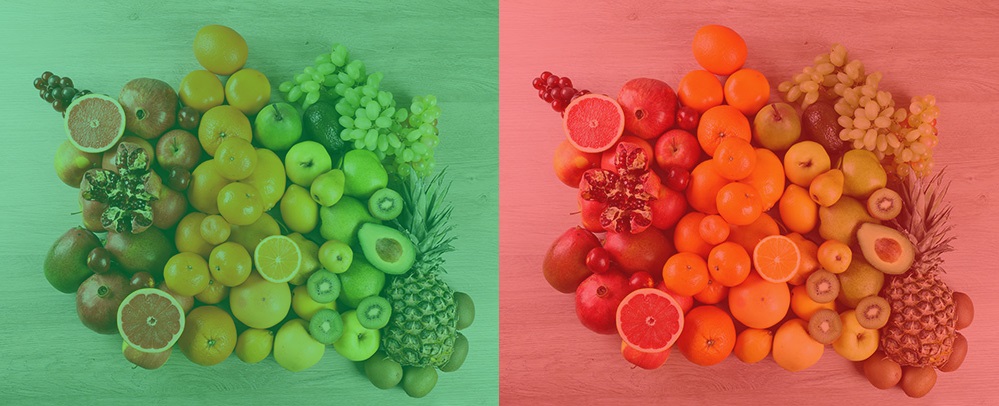
Practice 2: Demonstrating Color Constancy
Practice 2: Demonstrating Color Constancy
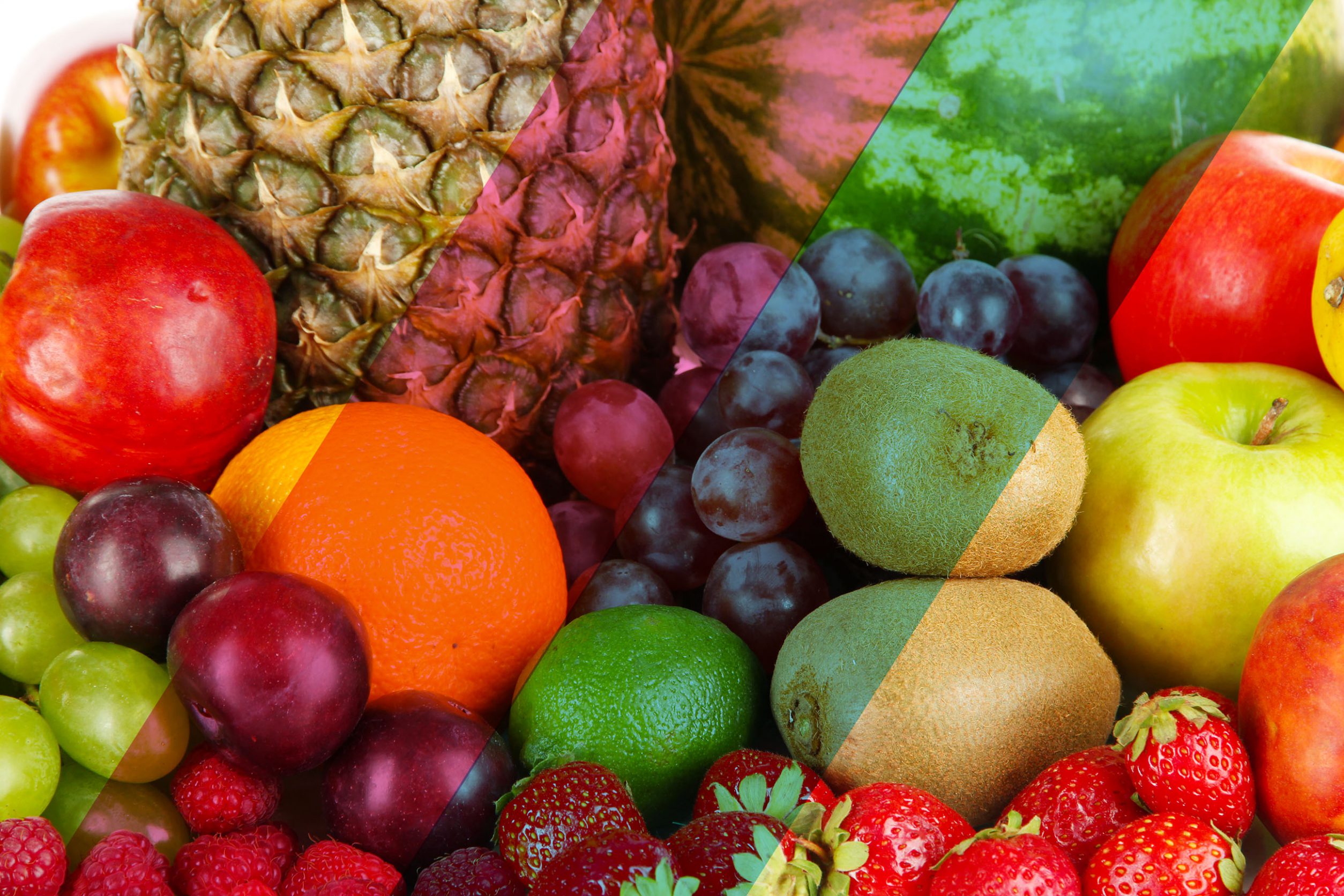
Use the buttons to vary the color of the beam of light, and observe the color of the fruit.

The principle of color constancy predicts that the perceived color of an object relative to other surrounding objects will not change when the color of the overhead lighting changes. Try it!
Notice that the actual light reflected from the fruit changes as the color of the light beam changes. But, we still perceive the lemon as "yellow" and the tomato as "red."
Light beam color:
Quiz 1
Quiz 1
Study the illustration and select an answer to the question. Then, select the CHECK ANSWER button.

Quiz 2
Quiz 2
Match the principles with the examples by dragging each term to the appropriate rectangle. When all the terms have been placed, select the CHECK ANSWER button.


Conclusion
